Resources
Explore a wide range of valuable resources on GCED to deepen your understanding and enhance your research, advocacy, teaching, and learning.
13 Results found
 Education Sector Analysis: Methodological Guidelines (Vol. 3) Year of publication: 2021 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) | Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (UK) This present volume is the third in a series of education sector analysis (ESA) guidelines following two volumes published in 2014. The series provides methodologies and applied examples for diagnosing education systems and informing national education policies and plans. This volume proposes guidelines to strengthen national capacities in analyzing education systems in four areas: inclusive education system for children with disabilities, risk analysis for resilient education systems, functioning and effectiveness of the educational administration, and stakeholder mapping and problem-driven analysis (governance and political economy).
Education Sector Analysis: Methodological Guidelines (Vol. 3) Year of publication: 2021 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) | Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (UK) This present volume is the third in a series of education sector analysis (ESA) guidelines following two volumes published in 2014. The series provides methodologies and applied examples for diagnosing education systems and informing national education policies and plans. This volume proposes guidelines to strengthen national capacities in analyzing education systems in four areas: inclusive education system for children with disabilities, risk analysis for resilient education systems, functioning and effectiveness of the educational administration, and stakeholder mapping and problem-driven analysis (governance and political economy).  Gender-responsive education sector planning: A pathway to gender equality in education Year of publication: 2019 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) | United Nations Girls' Education Initiative (UNGEI) Education transforms lives. It is the surest investment to break down social and economic differences between people, unravel inequalities based on gender and accelerate progress towards the entire vision of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Yet, despite the world’s commitment to ensure every child completes 12 years of quality education, in low-income countries only 4% of the poorest finish upper secondary school, falling to 2% among marginalized girls.Sustainable Development Goal 4, inclusive and equitable quality education for all, is about much more than education access. It calls for education policies to look beyond gender parity in school enrollment in order to put gender equality at the heart of education through gender-sensitive plans and policies. Gender-responsive education sector planning is an essential tool for advancing gender equality in and through education.
Gender-responsive education sector planning: A pathway to gender equality in education Year of publication: 2019 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) | United Nations Girls' Education Initiative (UNGEI) Education transforms lives. It is the surest investment to break down social and economic differences between people, unravel inequalities based on gender and accelerate progress towards the entire vision of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Yet, despite the world’s commitment to ensure every child completes 12 years of quality education, in low-income countries only 4% of the poorest finish upper secondary school, falling to 2% among marginalized girls.Sustainable Development Goal 4, inclusive and equitable quality education for all, is about much more than education access. It calls for education policies to look beyond gender parity in school enrollment in order to put gender equality at the heart of education through gender-sensitive plans and policies. Gender-responsive education sector planning is an essential tool for advancing gender equality in and through education. 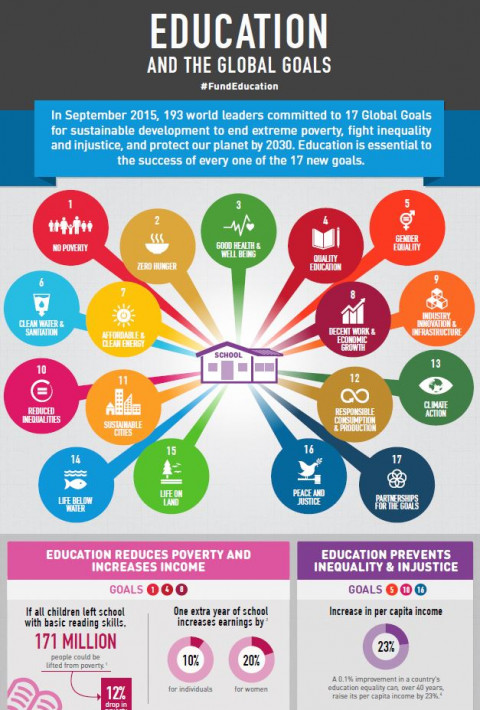 Education and the Global Goals Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) In September 2015, 193 world leaders committed to 17 Global Goals for sustainable development to end extreme poverty, fight inequality and injustice, and protect our planet by 2030. Education is essential to the success of every one of the 17 new goals.To learn more: https://www.globalpartnership.org/blog/17-ways-education-influences-new-17-global-goals
Education and the Global Goals Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) In September 2015, 193 world leaders committed to 17 Global Goals for sustainable development to end extreme poverty, fight inequality and injustice, and protect our planet by 2030. Education is essential to the success of every one of the 17 new goals.To learn more: https://www.globalpartnership.org/blog/17-ways-education-influences-new-17-global-goals  Education for All: Meeting the Challenges of the 21st Century Year of publication: 2017 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) In this speech at the London School of Economics on May 22 2017, Julia Gillard, Board Chair of the Global Partnership for Education, described the global education crisis that the world is facing, and how investing in inclusive, quality education is urgently needed to achieve sustainable development.
Education for All: Meeting the Challenges of the 21st Century Year of publication: 2017 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) In this speech at the London School of Economics on May 22 2017, Julia Gillard, Board Chair of the Global Partnership for Education, described the global education crisis that the world is facing, and how investing in inclusive, quality education is urgently needed to achieve sustainable development.  What Makes a Great Education? Year of publication: 2019 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) GPE works to strengthen national education systems to dramatically increase the number of children who are in school and learning.Since 2002, GPE has worked with more than 65 developing countries to improve education planning and implementation, with great results.
What Makes a Great Education? Year of publication: 2019 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) GPE works to strengthen national education systems to dramatically increase the number of children who are in school and learning.Since 2002, GPE has worked with more than 65 developing countries to improve education planning and implementation, with great results.  Global Partnership for Education Results Report 2018 Year of publication: 2018 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) The GPE Results Report 2018 shows progress against agreed-upon targets and identifies critical gaps that need to be addressed.
Global Partnership for Education Results Report 2018 Year of publication: 2018 Corporate author: Global Partnership for Education (GPE) The GPE Results Report 2018 shows progress against agreed-upon targets and identifies critical gaps that need to be addressed.  Guide pour l'évaluation d'un plan sectoriel d'éducation Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) At the World Education Forum, in Dakar in 2000, the international community pledged that no country with a credible plan to achieve the Education for All goals would be thwarted by a lack of resources. Since then, the development of an education sector plan (ESP) has become a priority in many countries. ESPs present the policies and strategies for national education reform, and are a powerful tool for coordinating partners and for mobilizing additional domestic and external resources. They have become a critical instrument for governments to signal to all potential investors that their education policies are credible, sustainable, and worthy of investment.The consensus on the need for credible ESPs is strong. However, what does a credible plan require in terms of government leadership, knowledge and data, institutional and human capacities, and dialogue among the education stakeholders? What are the criteria that establish the credibility of a plan? The purpose of these guidelines is to assist education stakeholders in appraising the soundness, relevance, and coherence that form the credibility of ESPs. The primary objective of an appraisal report is to support the finalization of a credible ESP. It provides a fair review of the ESP strengths and areas in need of improvement before the endorsement by partners which signifies their commitment to support the implementation of the ESP. These guidelines are meant to be adapted to national contexts and needs. The stakeholders should discuss the scope and the methodology of the appraisal to be used, and develop a common vision of the whole process. The appraisal process should be participatory, and grounded in the political and technical dialogue for ESP development. It should involve consultations, interviews with key stakeholders, and field visits, in addition to a desk review of the ESP and any other relevant documents. It is good practice to organize a validation workshop of the appraisal report’s findings, conclusions, and recommendations to feed into the ESP finalization. The appraisal process should occur early enough in the ESP development process to allow time for decision-makers to open consultations on these conclusions and recommendations in order to improve the final version of the ESP.
Guide pour l'évaluation d'un plan sectoriel d'éducation Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) At the World Education Forum, in Dakar in 2000, the international community pledged that no country with a credible plan to achieve the Education for All goals would be thwarted by a lack of resources. Since then, the development of an education sector plan (ESP) has become a priority in many countries. ESPs present the policies and strategies for national education reform, and are a powerful tool for coordinating partners and for mobilizing additional domestic and external resources. They have become a critical instrument for governments to signal to all potential investors that their education policies are credible, sustainable, and worthy of investment.The consensus on the need for credible ESPs is strong. However, what does a credible plan require in terms of government leadership, knowledge and data, institutional and human capacities, and dialogue among the education stakeholders? What are the criteria that establish the credibility of a plan? The purpose of these guidelines is to assist education stakeholders in appraising the soundness, relevance, and coherence that form the credibility of ESPs. The primary objective of an appraisal report is to support the finalization of a credible ESP. It provides a fair review of the ESP strengths and areas in need of improvement before the endorsement by partners which signifies their commitment to support the implementation of the ESP. These guidelines are meant to be adapted to national contexts and needs. The stakeholders should discuss the scope and the methodology of the appraisal to be used, and develop a common vision of the whole process. The appraisal process should be participatory, and grounded in the political and technical dialogue for ESP development. It should involve consultations, interviews with key stakeholders, and field visits, in addition to a desk review of the ESP and any other relevant documents. It is good practice to organize a validation workshop of the appraisal report’s findings, conclusions, and recommendations to feed into the ESP finalization. The appraisal process should occur early enough in the ESP development process to allow time for decision-makers to open consultations on these conclusions and recommendations in order to improve the final version of the ESP.  Guidelines for education sector plan appraisal (prs) Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیهیگانه تفاهمنامه چند جانبه جهانی است که جهت فراخواندن تمام اطفال در مکاتب با کیفیت وقف گردیده است. مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه حدودأ شامل دولت 60کشور رو به ترقی و همچنان کشور های حمایت کننده،نهاد های جامعه مدنی، نهاد های بین المللی، اتحادیه های خصوصی و معلمان، و سکتور خصوصی میباشد. این مشارکت منابع مالی را جهت حمایت انکشاف و تطبیق پلان های استراتیژیک با کیفیت در فقیر ترین کشور های جهان میباشد.مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه رهبری های ملی و بین المللی را دور هم جمع می نماید تا از آموزش هر طفل در یک فضای مصئون و مؤثر آموزشی حمایت گردد. با حمایت برنامه های انکشافی جهت رسیدن به اهداف تعلیمی یک کشور، مانند تساوی جنسیتی، نتایج با کیفیت آموزشی، و دسترسی همگانی به مکاتب ابتدائیه، مشارکت جهانی تعلیم وتربیه تضمین می کند که به قدر کافی در تعلیم و تربیه سرمایه گذاری میشود. ما از بهبود رسیدن به نتایج آموزشی از طریق گردهم آوردن شرکا میان هم تا پلان های استراتیژیک با کیفیت را ترتیبنمایند، از طریق سرمایه گذاری بالای بخش های مهم استراتیژیکی و نیازمند بودجه پلان استراتیژیک کشور ها و از طریق بسیج نمودن شرکای داخلی در کشور ها تا از مزیت نسبی شان استفاد بتوانند حمایت نموده ایم.مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه در دهه گذشته مبلغ 3.9میلیارد دالر را برای حمایت اصلاحات در تعلیم و تربیه بعضی فقیر ترین کشور های جهان تخصیص داده است. در سال 2014تقریبأ نیم از این سرمایه گذاری به کشور های نا امن و متاثر از جنگ داده شد.
Guidelines for education sector plan appraisal (prs) Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیهیگانه تفاهمنامه چند جانبه جهانی است که جهت فراخواندن تمام اطفال در مکاتب با کیفیت وقف گردیده است. مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه حدودأ شامل دولت 60کشور رو به ترقی و همچنان کشور های حمایت کننده،نهاد های جامعه مدنی، نهاد های بین المللی، اتحادیه های خصوصی و معلمان، و سکتور خصوصی میباشد. این مشارکت منابع مالی را جهت حمایت انکشاف و تطبیق پلان های استراتیژیک با کیفیت در فقیر ترین کشور های جهان میباشد.مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه رهبری های ملی و بین المللی را دور هم جمع می نماید تا از آموزش هر طفل در یک فضای مصئون و مؤثر آموزشی حمایت گردد. با حمایت برنامه های انکشافی جهت رسیدن به اهداف تعلیمی یک کشور، مانند تساوی جنسیتی، نتایج با کیفیت آموزشی، و دسترسی همگانی به مکاتب ابتدائیه، مشارکت جهانی تعلیم وتربیه تضمین می کند که به قدر کافی در تعلیم و تربیه سرمایه گذاری میشود. ما از بهبود رسیدن به نتایج آموزشی از طریق گردهم آوردن شرکا میان هم تا پلان های استراتیژیک با کیفیت را ترتیبنمایند، از طریق سرمایه گذاری بالای بخش های مهم استراتیژیکی و نیازمند بودجه پلان استراتیژیک کشور ها و از طریق بسیج نمودن شرکای داخلی در کشور ها تا از مزیت نسبی شان استفاد بتوانند حمایت نموده ایم.مشارکت جهانی برای تعلیم و تربیه در دهه گذشته مبلغ 3.9میلیارد دالر را برای حمایت اصلاحات در تعلیم و تربیه بعضی فقیر ترین کشور های جهان تخصیص داده است. در سال 2014تقریبأ نیم از این سرمایه گذاری به کشور های نا امن و متاثر از جنگ داده شد.  Guidelines for education sector plan appraisal Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) At the World Education Forum, in Dakar in 2000, the international community pledged that no country with a credible plan to achieve the Education for All goals would be thwarted by a lack of resources. Since then, the development of an education sector plan (ESP) has become a priority in many countries. ESPs present the policies and strategies for national education reform, and are a powerful tool for coordinating partners and for mobilizing additional domestic and external resources. They have become a critical instrument for governments to signal to all potential investors that their education policies are credible, sustainable, and worthy of investment.The consensus on the need for credible ESPs is strong. However, what does a credible plan require in terms of government leadership, knowledge and data, institutional and human capacities, and dialogue among the education stakeholders? What are the criteria that establish the credibility of a plan? The purpose of these guidelines is to assist education stakeholders in appraising the soundness, relevance, and coherence that form the credibility of ESPs. The primary objective of an appraisal report is to support the finalization of a credible ESP. It provides a fair review of the ESP strengths and areas in need of improvement before the endorsement by partners which signifies their commitment to support the implementation of the ESP. These guidelines are meant to be adapted to national contexts and needs. The stakeholders should discuss the scope and the methodology of the appraisal to be used, and develop a common vision of the whole process. The appraisal process should be participatory, and grounded in the political and technical dialogue for ESP development. It should involve consultations, interviews with key stakeholders, and field visits, in addition to a desk review of the ESP and any other relevant documents. It is good practice to organize a validation workshop of the appraisal report’s findings, conclusions, and recommendations to feed into the ESP finalization. The appraisal process should occur early enough in the ESP development process to allow time for decision-makers to open consultations on these conclusions and recommendations in order to improve the final version of the ESP.
Guidelines for education sector plan appraisal Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) At the World Education Forum, in Dakar in 2000, the international community pledged that no country with a credible plan to achieve the Education for All goals would be thwarted by a lack of resources. Since then, the development of an education sector plan (ESP) has become a priority in many countries. ESPs present the policies and strategies for national education reform, and are a powerful tool for coordinating partners and for mobilizing additional domestic and external resources. They have become a critical instrument for governments to signal to all potential investors that their education policies are credible, sustainable, and worthy of investment.The consensus on the need for credible ESPs is strong. However, what does a credible plan require in terms of government leadership, knowledge and data, institutional and human capacities, and dialogue among the education stakeholders? What are the criteria that establish the credibility of a plan? The purpose of these guidelines is to assist education stakeholders in appraising the soundness, relevance, and coherence that form the credibility of ESPs. The primary objective of an appraisal report is to support the finalization of a credible ESP. It provides a fair review of the ESP strengths and areas in need of improvement before the endorsement by partners which signifies their commitment to support the implementation of the ESP. These guidelines are meant to be adapted to national contexts and needs. The stakeholders should discuss the scope and the methodology of the appraisal to be used, and develop a common vision of the whole process. The appraisal process should be participatory, and grounded in the political and technical dialogue for ESP development. It should involve consultations, interviews with key stakeholders, and field visits, in addition to a desk review of the ESP and any other relevant documents. It is good practice to organize a validation workshop of the appraisal report’s findings, conclusions, and recommendations to feed into the ESP finalization. The appraisal process should occur early enough in the ESP development process to allow time for decision-makers to open consultations on these conclusions and recommendations in order to improve the final version of the ESP.  Guía para la evaluación de un plan sectorial de educación Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) La Alianza Mundial para la Educación (GPE, por sus siglas en inglés) es la única alianza multilateral global cuya misión es conseguir que todos los niños y niñas estén escolarizados en un sistema educativo de calidad. La Alianza Mundial para la Educación engloba a alrededor de 60 gobiernos de países en desarrollo, así como a gobiernos socios, organizaciones de la sociedad civil, instituciones internacionales, profesores, fundaciones privadas y sector privado. Proporciona financiación para apoyar el diseño y la ejecución de planes sectoriales de educación de calidad en los países más pobres del mundo. La GPE reúne a líderes mundiales y nacionales para apoyar estrategias coordinadas que ofrezcan a todos los niños y niñas la oportunidad de aprender en un entorno de aprendizaje seguro y adecuado. La Alianza Global, mediante el apoyo a programas de desarrollo enfocados a alcanzar las metas educativas de cada país, tales como la paridad de género, resultados de aprendizaje de calidad y acceso universal a la educación primaria, garantiza que la inversión en educación valga la pena. Hemos ayudado a mejorar los resultados nacionales en educación gracias al trabajo conjunto de socios en la elaboración de planes sectoriales de educación, medibles y de calidad, a la inversión en componentes del plan que eran estratégicamente importantes y que no estaban suficientemente financiados y a la activación del expertise de socios en el país que han aportado su ventaja comparativa. La Alianza Mundial para la Educación ha asignado 3.900 millones de dólares en los últimos diez años para apoyar reformas educativas en los países más pobres de mundo. Prácticamente lamitad de la financiación de 2014 se destinó a estados frágiles o países en situación de conflicto.
Guía para la evaluación de un plan sectorial de educación Year of publication: 2015 Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Educational Planning (IIEP) | Global Partnership for Education (GPE) La Alianza Mundial para la Educación (GPE, por sus siglas en inglés) es la única alianza multilateral global cuya misión es conseguir que todos los niños y niñas estén escolarizados en un sistema educativo de calidad. La Alianza Mundial para la Educación engloba a alrededor de 60 gobiernos de países en desarrollo, así como a gobiernos socios, organizaciones de la sociedad civil, instituciones internacionales, profesores, fundaciones privadas y sector privado. Proporciona financiación para apoyar el diseño y la ejecución de planes sectoriales de educación de calidad en los países más pobres del mundo. La GPE reúne a líderes mundiales y nacionales para apoyar estrategias coordinadas que ofrezcan a todos los niños y niñas la oportunidad de aprender en un entorno de aprendizaje seguro y adecuado. La Alianza Global, mediante el apoyo a programas de desarrollo enfocados a alcanzar las metas educativas de cada país, tales como la paridad de género, resultados de aprendizaje de calidad y acceso universal a la educación primaria, garantiza que la inversión en educación valga la pena. Hemos ayudado a mejorar los resultados nacionales en educación gracias al trabajo conjunto de socios en la elaboración de planes sectoriales de educación, medibles y de calidad, a la inversión en componentes del plan que eran estratégicamente importantes y que no estaban suficientemente financiados y a la activación del expertise de socios en el país que han aportado su ventaja comparativa. La Alianza Mundial para la Educación ha asignado 3.900 millones de dólares en los últimos diez años para apoyar reformas educativas en los países más pobres de mundo. Prácticamente lamitad de la financiación de 2014 se destinó a estados frágiles o países en situación de conflicto. 