Resources
Explore a wide range of valuable resources on GCED to deepen your understanding and enhance your research, advocacy, teaching, and learning.
19 Results found
 مرحلة ما بعد عام 2015: التعليم الذي نصبو إليه Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.
مرحلة ما بعد عام 2015: التعليم الذي نصبو إليه Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.  Más allá de 2015: la educación que queremos Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.
Más allá de 2015: la educación que queremos Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.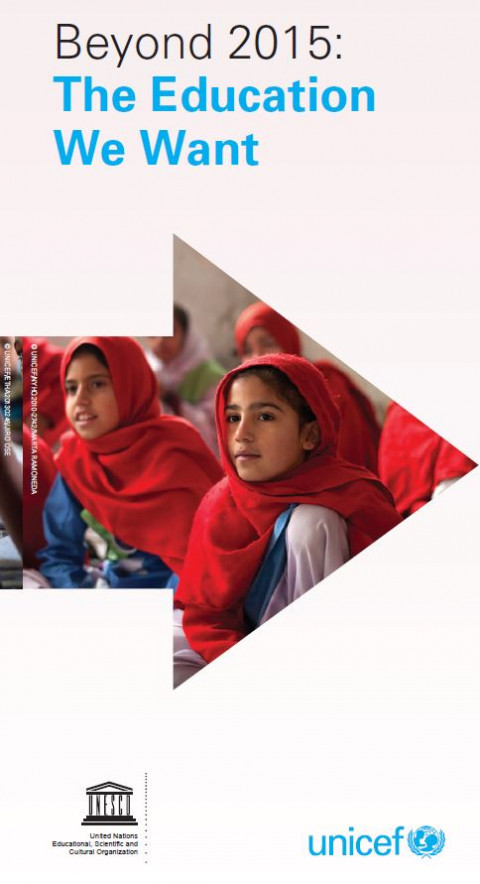  Beyond 2015: the education we want Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education.It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.
Beyond 2015: the education we want Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education.It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.  L'Après-2015: l'éducation que nous voulons Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.
L'Après-2015: l'éducation que nous voulons Year of publication: 2014 Corporate author: UNESCO | United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) The post-2015 education agenda should be aspirational, transformative and holistic, and an integral part of the broader post-2015 development agenda. It should be of universal relevance and mobilize all stakeholders in all countries. Education must be a stand-alone goal in the broader post-2015 development agenda and should be framed by a comprehensive overarching goal, with measurable global targets and related indicators. In addition, education must be integrated into other development goals. The future education agenda should be rights-based and reflect a perspective based on equity and inclusion, with particular attention to gender equality and to overcoming all forms of discrimination in and through education, ensuring that no-one is left behind. It must support free and compulsory basic education. It should expand the vision of access for all to reflect relevant learning outcomes through the provision of quality education at all levels, from early childhood to higher education, in safe and healthy environments. It should take a holistic and lifelong learning approach, and provide multiple pathways of learning using innovative methods and information and communication technologies. It should reinforce approaches such as global citizenship education and education for sustainable development, which foster attitudes and behaviours that promote peace, conflict resolution and mutual understanding, tolerance, critical thinking, and respect for cultural diversity and for the environment.  Measurement of global citizenship education Year of publication: 2013 Author: Vegard Skirbekk | Michaela Potančoková | Marcin Stonawski Corporate author: UNESCO In this study we provide an overview of Global Citizenship Education, focusing on definitions, methodological advances and data. We present an assessment of some of the existing initiatives for the measurement Global Citizenship Education, and make suggestions for how to move towards a globally consistent measure. Although there is some disagreement over how to measure global citizenship and global citizenship education, we also find consensus on parts of the concept. We are proposing to construct a composite indicator consisting of three complementary levels – the societal level (e.g., the level of democracy; macro level indicators of openness), the supplier level (e.g., provision of education; availability of training relevant for global citizenship); and the receiver level (civic identity, values, skills and knowledge). We conclude that one potential cost-effective approach could be to integrate evidence from several nationally representative surveys, providing us with world-wide coverage. We also discuss the feasibility and benefits of this measurement approach as well as its challenges.
Measurement of global citizenship education Year of publication: 2013 Author: Vegard Skirbekk | Michaela Potančoková | Marcin Stonawski Corporate author: UNESCO In this study we provide an overview of Global Citizenship Education, focusing on definitions, methodological advances and data. We present an assessment of some of the existing initiatives for the measurement Global Citizenship Education, and make suggestions for how to move towards a globally consistent measure. Although there is some disagreement over how to measure global citizenship and global citizenship education, we also find consensus on parts of the concept. We are proposing to construct a composite indicator consisting of three complementary levels – the societal level (e.g., the level of democracy; macro level indicators of openness), the supplier level (e.g., provision of education; availability of training relevant for global citizenship); and the receiver level (civic identity, values, skills and knowledge). We conclude that one potential cost-effective approach could be to integrate evidence from several nationally representative surveys, providing us with world-wide coverage. We also discuss the feasibility and benefits of this measurement approach as well as its challenges.  Measurement of global citizenship education Year of publication: 2013 Author: Vegard Skirbekk | Michaela Potančoková | Marcin Stonawski Corporate author: UNESCO Dans cette étude, nous présentons un aperçu de l’Éducation à la Citoyenneté Mondiale, en se concentrant sur les définitions, les progrès méthodologiques et des données. Nous présentons une évaluation de quelques-unes des initiatives existantes pour la mesure d'éducation à la citoyenneté mondiale, et de faire des suggestions sur la façon de progresser vers une mesure cohérente au niveau mondial. Bien qu'il y ait un certain désaccord sur la façon de mesurer la citoyenneté mondiale et de l'éducation à la citoyenneté mondiale, on trouve aussi un consensus sur certaines parties du concept. Nous proposons de construire un indicateur composite constitué de trois niveaux complémentaires - le niveau de la société (par exemple, le niveau de la démocratie, les indicateurs macro-niveau d'ouverture), le niveau des fournisseurs (par exemple, la fourniture de l'éducation, la disponibilité de la formation pertinente à la citoyenneté mondiale) ; et le niveau du récepteur (identité civique, les valeurs, les compétences et les connaissances). Nous concluons qu'une approche potentielle rentable pourrait être d'intégrer des preuves de plusieurs enquêtes représentatives au niveau national, nous fournissant une couverture mondiale. Nous discutons aussi la faisabilité et les avantages de cette approche de mesures ainsi que ses défis.
Measurement of global citizenship education Year of publication: 2013 Author: Vegard Skirbekk | Michaela Potančoková | Marcin Stonawski Corporate author: UNESCO Dans cette étude, nous présentons un aperçu de l’Éducation à la Citoyenneté Mondiale, en se concentrant sur les définitions, les progrès méthodologiques et des données. Nous présentons une évaluation de quelques-unes des initiatives existantes pour la mesure d'éducation à la citoyenneté mondiale, et de faire des suggestions sur la façon de progresser vers une mesure cohérente au niveau mondial. Bien qu'il y ait un certain désaccord sur la façon de mesurer la citoyenneté mondiale et de l'éducation à la citoyenneté mondiale, on trouve aussi un consensus sur certaines parties du concept. Nous proposons de construire un indicateur composite constitué de trois niveaux complémentaires - le niveau de la société (par exemple, le niveau de la démocratie, les indicateurs macro-niveau d'ouverture), le niveau des fournisseurs (par exemple, la fourniture de l'éducation, la disponibilité de la formation pertinente à la citoyenneté mondiale) ; et le niveau du récepteur (identité civique, les valeurs, les compétences et les connaissances). Nous concluons qu'une approche potentielle rentable pourrait être d'intégrer des preuves de plusieurs enquêtes représentatives au niveau national, nous fournissant une couverture mondiale. Nous discutons aussi la faisabilité et les avantages de cette approche de mesures ainsi que ses défis. 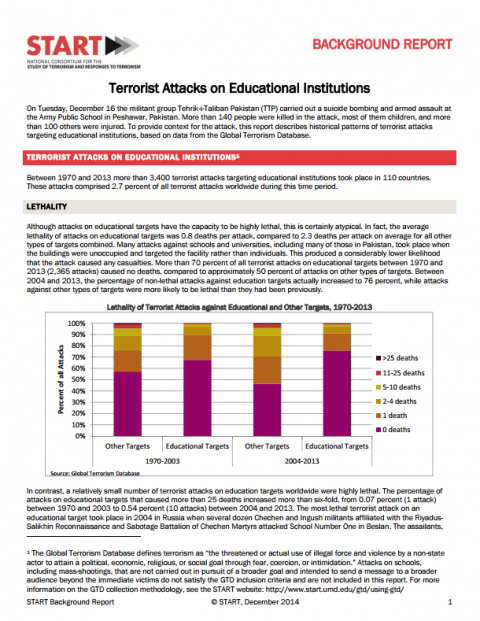 Terrorist Attacks on Educational Institutions Year of publication: 2014 Author: Erin Miller Corporate author: National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) | Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology The report describes historical patterns of terrorist attacks targeting educations institutions dating back to 1970. Since that year, more than 3,400 terrorist attacks targeting educations institutions took place in 110 countries. These attacks comprised 2.7 percent of all terrorist attacks worldwide during this time period.
Terrorist Attacks on Educational Institutions Year of publication: 2014 Author: Erin Miller Corporate author: National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) | Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology The report describes historical patterns of terrorist attacks targeting educations institutions dating back to 1970. Since that year, more than 3,400 terrorist attacks targeting educations institutions took place in 110 countries. These attacks comprised 2.7 percent of all terrorist attacks worldwide during this time period.  Terrorist Attacks on Educational Institutions Year of publication: 2014 Author: Erin Miller Corporate author: National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) | Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Le rapport revient sur les attaques terroristes qui ont ciblé les institutions éducatives depuis 1970. A partir de cette année, on dénombre plus de 3.400 attaques terroristes qui avaient pour cible les institutions éducatives, dans 110 pays. Ces attaques représentent 2,7 % de l’ensemble des attaques terroristes perpétrées à travers le monde au cours de cette période.
Terrorist Attacks on Educational Institutions Year of publication: 2014 Author: Erin Miller Corporate author: National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (START) | Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Le rapport revient sur les attaques terroristes qui ont ciblé les institutions éducatives depuis 1970. A partir de cette année, on dénombre plus de 3.400 attaques terroristes qui avaient pour cible les institutions éducatives, dans 110 pays. Ces attaques représentent 2,7 % de l’ensemble des attaques terroristes perpétrées à travers le monde au cours de cette période.  Panorámica regional: América Latina y el Caribe Year of publication: 2011 Corporate author: UNESCO The past decade has seen mixed progress towards Education for All (EFA) in Latin America and the Caribbean. More children are participating in pre-school education, many countries have achieved universal primary education and more students are moving from primary to secondary education. Gender parity has been achieved at the primary level in the majority of countries and adult literacy rates are improving. The region invests a relatively high share of national income in education and external aid to basic education has increased in recent years. However, challenges remain. The Caribbean has seen a decline by nearly one-tenth in primary enrolment ratios and 2.9 million children were not enrolled in school in the region as a whole in 2008. Some 36 million adults are still illiterate and levels of learning achievement are low in many countries. The 2011 EFA Global Monitoring Report puts the spotlight on armed conflict and one of its most damaging yet least reported consequences: its impact on education. Conflict-affected states have some of the world’s worst indicators for education. The Report documents the scale of this hidden crisis in education, looks at its underlying causes and explores the links between armed conflict and education. It also presents recommendations to address identified failures that contribute to the hidden crisis. It calls on governments to demonstrate greater resolve in combating the culture of impunity surrounding attacks on schoolchildren and schools, sets out an agenda for fixing the international aid architecture and identifies strategies for strengthening the role of education in peacebuilding.
Panorámica regional: América Latina y el Caribe Year of publication: 2011 Corporate author: UNESCO The past decade has seen mixed progress towards Education for All (EFA) in Latin America and the Caribbean. More children are participating in pre-school education, many countries have achieved universal primary education and more students are moving from primary to secondary education. Gender parity has been achieved at the primary level in the majority of countries and adult literacy rates are improving. The region invests a relatively high share of national income in education and external aid to basic education has increased in recent years. However, challenges remain. The Caribbean has seen a decline by nearly one-tenth in primary enrolment ratios and 2.9 million children were not enrolled in school in the region as a whole in 2008. Some 36 million adults are still illiterate and levels of learning achievement are low in many countries. The 2011 EFA Global Monitoring Report puts the spotlight on armed conflict and one of its most damaging yet least reported consequences: its impact on education. Conflict-affected states have some of the world’s worst indicators for education. The Report documents the scale of this hidden crisis in education, looks at its underlying causes and explores the links between armed conflict and education. It also presents recommendations to address identified failures that contribute to the hidden crisis. It calls on governments to demonstrate greater resolve in combating the culture of impunity surrounding attacks on schoolchildren and schools, sets out an agenda for fixing the international aid architecture and identifies strategies for strengthening the role of education in peacebuilding.  Regional overview: Latin America and the Caribbean Year of publication: 2011 Corporate author: UNESCO The past decade has seen mixed progress towards Education for All (EFA) in Latin America and the Caribbean. More children are participating in pre-school education, many countries have achieved universal primary education and more students are moving from primary to secondary education. Gender parity has been achieved at the primary level in the majority of countries and adult literacy rates are improving. The region invests a relatively high share of national income in education and external aid to basic education has increased in recent years. However, challenges remain. The Caribbean has seen a decline by nearly one-tenth in primary enrolment ratios and 2.9 million children were not enrolled in school in the region as a whole in 2008. Some 36 million adults are still illiterate and levels of learning achievement are low in many countries. The 2011 EFA Global Monitoring Report puts the spotlight on armed conflict and one of its most damaging yet least reported consequences: its impact on education. Conflict-affected states have some of the world’s worst indicators for education. The Report documents the scale of this hidden crisis in education, looks at its underlying causes and explores the links between armed conflict and education. It also presents recommendations to address identified failures that contribute to the hidden crisis. It calls on governments to demonstrate greater resolve in combating the culture of impunity surrounding attacks on schoolchildren and schools, sets out an agenda for fixing the international aid architecture and identifies strategies for strengthening the role of education in peacebuilding.
Regional overview: Latin America and the Caribbean Year of publication: 2011 Corporate author: UNESCO The past decade has seen mixed progress towards Education for All (EFA) in Latin America and the Caribbean. More children are participating in pre-school education, many countries have achieved universal primary education and more students are moving from primary to secondary education. Gender parity has been achieved at the primary level in the majority of countries and adult literacy rates are improving. The region invests a relatively high share of national income in education and external aid to basic education has increased in recent years. However, challenges remain. The Caribbean has seen a decline by nearly one-tenth in primary enrolment ratios and 2.9 million children were not enrolled in school in the region as a whole in 2008. Some 36 million adults are still illiterate and levels of learning achievement are low in many countries. The 2011 EFA Global Monitoring Report puts the spotlight on armed conflict and one of its most damaging yet least reported consequences: its impact on education. Conflict-affected states have some of the world’s worst indicators for education. The Report documents the scale of this hidden crisis in education, looks at its underlying causes and explores the links between armed conflict and education. It also presents recommendations to address identified failures that contribute to the hidden crisis. It calls on governments to demonstrate greater resolve in combating the culture of impunity surrounding attacks on schoolchildren and schools, sets out an agenda for fixing the international aid architecture and identifies strategies for strengthening the role of education in peacebuilding. 