Resources
Explore a wide range of valuable resources on GCED to deepen your understanding and enhance your research, advocacy, teaching, and learning.
881 Results found
 Guía de recursos digitales: Educación mediática contra el discurso de odio Year of publication: 2022 Corporate author: Esplai Foundation Podríamos definir el discurso de odio como el conjunto de acciones comunicativas orientadas a la defensa, promoción o instigación al odio, la humillación o el menosprecio de una persona o grupo de personas. Si bien el discurso de odio no es algo exclusivo de Internet, sino que es parte de la realidad más allá de las redes, es cierto que el potencial de las redes facilita el movimiento de los flujos comunicativos, porque facilita tanto la producción como la creación de mensajes. Los discursos de odio también se han visto beneficiados por esto y, además, han encontrado en las redes otras características como el anonimato, la brevedad, los servicios gratuitos de mensajería o la legitimidad otorgada por número de seguidores. Con esta guía queremos aportar herramientas digitales para la creación de ese contradiscurso que permita realizar mensajes que ofrecen una alternativa positiva a la propaganda extremista.
Guía de recursos digitales: Educación mediática contra el discurso de odio Year of publication: 2022 Corporate author: Esplai Foundation Podríamos definir el discurso de odio como el conjunto de acciones comunicativas orientadas a la defensa, promoción o instigación al odio, la humillación o el menosprecio de una persona o grupo de personas. Si bien el discurso de odio no es algo exclusivo de Internet, sino que es parte de la realidad más allá de las redes, es cierto que el potencial de las redes facilita el movimiento de los flujos comunicativos, porque facilita tanto la producción como la creación de mensajes. Los discursos de odio también se han visto beneficiados por esto y, además, han encontrado en las redes otras características como el anonimato, la brevedad, los servicios gratuitos de mensajería o la legitimidad otorgada por número de seguidores. Con esta guía queremos aportar herramientas digitales para la creación de ese contradiscurso que permita realizar mensajes que ofrecen una alternativa positiva a la propaganda extremista.  الاستراتيجيات التعليمية لتعلم مهارات حل النزاعات في المدرسة (مجلة المستنصرية للعلوم الإنسانية؛ Vol. 1-1، العدد الخاص) Year of publication: 2023 Author: Haider Kareem Sukar Corporate author: Mustansiriyah University تعد المدرسة إحدى أدوات المجتمع التي تحقق أهدافه التربوية من خلال جميع العادات السلوكية التي تؤمن للتلاميذ النمو السليم والمتكامل الى جانب الإعداد والتكيف للمستقبل بعد الحصول على النجاح والانخراط في مؤسسات الدولة او مزاولة النشاط الاقتصادي ويتعدى الأمر الى أكثر من ذلك في كثير من الأحيان بحيث يتشكل من خلال التعليم ابرز ملامح المجتمع وتتحدد مكانته في السلم الحضاري، لذا على المدرسة تحقيق جميع ذلك من خلال وسائل وفلسفة تربوية قائمة على أسس معرفية تقوم الجهات التربوية المختصة بتحديدها. وقد يسعى الابناء المراهقون نحو مزيد من الحرية والسلطة والتحرر الكامل فيما بعد من سلطة الوالدين والاخرين الممثلة بالمدرسة كونها البيئة الاوسع بعد الاسرة التي تحتضن الشخص، لذا نرى هؤلاء الابناء يقومون باعمال مثل الاساءة للغير وخرق النظام والقانون والغلظة في التعامل مع غيرهم او الوقاحة في تصرفهم معهم، وقد يرتكبون اخطاء ويسيئون التصرف عن عمد على الرغم من انهم يعرفون الصواب وقادرون على التصرف الحسن. لهذا فقد ادى تزايد مظاهر العنف والخلاف والنزاع في المدارس الى ازدياد اهتمام المربين على اختلاف مراكزهم لعملية تعلم وتعليم التلاميذ لمفاهيم حقوق الانسان واتجاهات التسامح بعامة ومهارات حل الخلافات والنزاعات باساليب وطرائق بناءة وايجابية.
الاستراتيجيات التعليمية لتعلم مهارات حل النزاعات في المدرسة (مجلة المستنصرية للعلوم الإنسانية؛ Vol. 1-1، العدد الخاص) Year of publication: 2023 Author: Haider Kareem Sukar Corporate author: Mustansiriyah University تعد المدرسة إحدى أدوات المجتمع التي تحقق أهدافه التربوية من خلال جميع العادات السلوكية التي تؤمن للتلاميذ النمو السليم والمتكامل الى جانب الإعداد والتكيف للمستقبل بعد الحصول على النجاح والانخراط في مؤسسات الدولة او مزاولة النشاط الاقتصادي ويتعدى الأمر الى أكثر من ذلك في كثير من الأحيان بحيث يتشكل من خلال التعليم ابرز ملامح المجتمع وتتحدد مكانته في السلم الحضاري، لذا على المدرسة تحقيق جميع ذلك من خلال وسائل وفلسفة تربوية قائمة على أسس معرفية تقوم الجهات التربوية المختصة بتحديدها. وقد يسعى الابناء المراهقون نحو مزيد من الحرية والسلطة والتحرر الكامل فيما بعد من سلطة الوالدين والاخرين الممثلة بالمدرسة كونها البيئة الاوسع بعد الاسرة التي تحتضن الشخص، لذا نرى هؤلاء الابناء يقومون باعمال مثل الاساءة للغير وخرق النظام والقانون والغلظة في التعامل مع غيرهم او الوقاحة في تصرفهم معهم، وقد يرتكبون اخطاء ويسيئون التصرف عن عمد على الرغم من انهم يعرفون الصواب وقادرون على التصرف الحسن. لهذا فقد ادى تزايد مظاهر العنف والخلاف والنزاع في المدارس الى ازدياد اهتمام المربين على اختلاف مراكزهم لعملية تعلم وتعليم التلاميذ لمفاهيم حقوق الانسان واتجاهات التسامح بعامة ومهارات حل الخلافات والنزاعات باساليب وطرائق بناءة وايجابية.  Instructional Strategies for Learning Conflict Resolution Skills in School (Mustansiriyah Journal of Humanities; Vol. 1-1, Special Issue) Year of publication: 2023 Author: Haider Kareem Sukar Corporate author: Mustansiriyah University The school is a community tool that achieves its educational goals through all behavioral habits that provide students with sound and integrated growth, as well as preparation and adaptation for the future after obtaining success and involvement in government institutions and the economy. In the civilizational scale, so the school must achieve all means of education and an educational philosophy based on foundations with educational entertainment Adolescent children may seek more freedom, power, and complete liberation later on from the authority of parents and others represented by the school, as it is the broader environment after the family that embraces the person, so we see these children doing actions such as abuse of others, violation of order and law, harshness in dealing with others, or rudeness in their behavior with them They may make mistakes and misbehave on purpose even though they know what is right and are able to act well. Therefore, the increasing manifestations of violence, disagreement and conflict in schools have led to an increase in the interest of educators of all positions in the process of learning and teaching students the concepts of human rights and the attitudes of tolerance in general and the skills of resolving differences and conflicts in constructive and positive ways and means.
Instructional Strategies for Learning Conflict Resolution Skills in School (Mustansiriyah Journal of Humanities; Vol. 1-1, Special Issue) Year of publication: 2023 Author: Haider Kareem Sukar Corporate author: Mustansiriyah University The school is a community tool that achieves its educational goals through all behavioral habits that provide students with sound and integrated growth, as well as preparation and adaptation for the future after obtaining success and involvement in government institutions and the economy. In the civilizational scale, so the school must achieve all means of education and an educational philosophy based on foundations with educational entertainment Adolescent children may seek more freedom, power, and complete liberation later on from the authority of parents and others represented by the school, as it is the broader environment after the family that embraces the person, so we see these children doing actions such as abuse of others, violation of order and law, harshness in dealing with others, or rudeness in their behavior with them They may make mistakes and misbehave on purpose even though they know what is right and are able to act well. Therefore, the increasing manifestations of violence, disagreement and conflict in schools have led to an increase in the interest of educators of all positions in the process of learning and teaching students the concepts of human rights and the attitudes of tolerance in general and the skills of resolving differences and conflicts in constructive and positive ways and means.  3rd Global Forum Against Racism and Discrimination: Final Document Year of publication: 2024 Corporate author: UNESCO The third edition of the Global Forum against Racism and Discrimination with the theme “Race to the top: putting racial equity and justice at the forefront of development agendas” was held in São Paulo, Brazil, on 29 November 2023 and 1 December 2023. At the invitation of Brazil, in partnership with the Ford Foundation, the Open Society Foundations, the Mover Foundation, Instituto Ibirapitanga, the Global Forum highlighted the importance of placing racial issues at the core of development and implementation strategies, with a view to socioeconomic development. The Global Forum welcomed Ministers, high-ranking officials of national bodies responsible for combating discrimination and promoting equality, mayors of the International Coalition of Inclusive and Sustainable Cities - ICCAR, academics, scientists, civil society actors, NGOs, artists and digital influencers to share good practices, strengthen commitments and discuss effective strategies to combat racism and various forms of discriminations, including recommendations on how to proceed. The Global Forum’s agenda covered several topics, such as co-creating inclusive policies with impacted communities’ inputs; increasing awareness-raising on historical systems such as transatlantic enslavement to better comprehend and dismantle their contemporary legacies such as racism; progress towards gender equality; enhancing the capacities of civil society to be an agent of change; addressing artificial intelligence and its role in perpetuating racism; protecting the rights of indigenous peoples; establishing legal and policy frameworks prioritizing anti-racism and anti-discrimination on a local and global scale; strengthening the roles of cities, civic spaces, artistic and academic communities; enhancing the importance of informed data baseline on equality for governments; and promoting social philanthropy to address racial inequality. The 2023 edition was also marked by the launch of new initiatives. One of the main outcomes of the Global Forum is the establishment of the UNESCO Network of Anti-Racism and Anti-Discrimination Officials aiming to strengthen the development of innovative and inclusive policy solutions for peace, equity and non-discrimination. UNESCO has launched the new UNESCO Anti-Racism Toolkit, the Gender-Based Resilience Framework, the ‘Let’s Talk‘ project with Harvard University to combat prejudice against migrants, and the development of a new joint OECD-UNESCO briefing on combating discrimination against migrants. Volume X of the UNESCO General History of Africa, entitled Africa and its Diasporas, was also launched during the Global Forum. The publication offers a mapping of African diasporas throughout the world, valorizing their contributions to modern societies.
3rd Global Forum Against Racism and Discrimination: Final Document Year of publication: 2024 Corporate author: UNESCO The third edition of the Global Forum against Racism and Discrimination with the theme “Race to the top: putting racial equity and justice at the forefront of development agendas” was held in São Paulo, Brazil, on 29 November 2023 and 1 December 2023. At the invitation of Brazil, in partnership with the Ford Foundation, the Open Society Foundations, the Mover Foundation, Instituto Ibirapitanga, the Global Forum highlighted the importance of placing racial issues at the core of development and implementation strategies, with a view to socioeconomic development. The Global Forum welcomed Ministers, high-ranking officials of national bodies responsible for combating discrimination and promoting equality, mayors of the International Coalition of Inclusive and Sustainable Cities - ICCAR, academics, scientists, civil society actors, NGOs, artists and digital influencers to share good practices, strengthen commitments and discuss effective strategies to combat racism and various forms of discriminations, including recommendations on how to proceed. The Global Forum’s agenda covered several topics, such as co-creating inclusive policies with impacted communities’ inputs; increasing awareness-raising on historical systems such as transatlantic enslavement to better comprehend and dismantle their contemporary legacies such as racism; progress towards gender equality; enhancing the capacities of civil society to be an agent of change; addressing artificial intelligence and its role in perpetuating racism; protecting the rights of indigenous peoples; establishing legal and policy frameworks prioritizing anti-racism and anti-discrimination on a local and global scale; strengthening the roles of cities, civic spaces, artistic and academic communities; enhancing the importance of informed data baseline on equality for governments; and promoting social philanthropy to address racial inequality. The 2023 edition was also marked by the launch of new initiatives. One of the main outcomes of the Global Forum is the establishment of the UNESCO Network of Anti-Racism and Anti-Discrimination Officials aiming to strengthen the development of innovative and inclusive policy solutions for peace, equity and non-discrimination. UNESCO has launched the new UNESCO Anti-Racism Toolkit, the Gender-Based Resilience Framework, the ‘Let’s Talk‘ project with Harvard University to combat prejudice against migrants, and the development of a new joint OECD-UNESCO briefing on combating discrimination against migrants. Volume X of the UNESCO General History of Africa, entitled Africa and its Diasporas, was also launched during the Global Forum. The publication offers a mapping of African diasporas throughout the world, valorizing their contributions to modern societies.  Lessons from a Transformative Pedagogy Project for Peace, Resilience, and the Prevention of Violent Extremism: Part I; Country-Level Implementation Year of publication: 2024 Author: Eyerusalem Azmeraw | Quentin Wodon | Eleonora Mura | Kasumi Moritani Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Capacity-Building in Africa (IICBA) From 2017 to 2022, UNESCO’s International Institute for Capacity Building in Africa (IICBA) led a series of projects for peacebuilding and the prevention of violent extremism through education with support from the Government of Japan. This two-part paper draws lessons from the projects. The first part of the paper briefly explains the transformative pedagogy approach that guided project implementation and provides examples of changes that were implemented at the country level under the projects. The analysis is qualitative, with the aim being to outline, through country examples, what can be achieved through such projects. Lessons on factors contributing to impact are also outlined.
Lessons from a Transformative Pedagogy Project for Peace, Resilience, and the Prevention of Violent Extremism: Part I; Country-Level Implementation Year of publication: 2024 Author: Eyerusalem Azmeraw | Quentin Wodon | Eleonora Mura | Kasumi Moritani Corporate author: UNESCO International Institute for Capacity-Building in Africa (IICBA) From 2017 to 2022, UNESCO’s International Institute for Capacity Building in Africa (IICBA) led a series of projects for peacebuilding and the prevention of violent extremism through education with support from the Government of Japan. This two-part paper draws lessons from the projects. The first part of the paper briefly explains the transformative pedagogy approach that guided project implementation and provides examples of changes that were implemented at the country level under the projects. The analysis is qualitative, with the aim being to outline, through country examples, what can be achieved through such projects. Lessons on factors contributing to impact are also outlined.  United Nations Strategy and Plan of Action on Hate Speech: Detailed Guidance on Implementation for United Nations Field Presences Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: United Nations (UN) The Strategy and Plan of Action acknowledges that hate speech has the potential to incite violence and undermine social unity. It recognizes that hate speech has been a precursor to atrocity crimes, including genocide, over the past 75 years. This approach to coordinating efforts across the UN system to identify, prevent and confront hate speech is grounded in international human rights standards, including the right to freedom of opinion and expression, principles of equality and non-discrimination, as well as other fundamental rights. The Strategy aims to give the United Nations the room and the resources to address hate speech, which poses a threat to UN principles, values and programmes. It guides the UN system on how to address hate speech and includes ways to support United Nations Resident Coordinators’ action in addressing and countering hate speech on the ground.
United Nations Strategy and Plan of Action on Hate Speech: Detailed Guidance on Implementation for United Nations Field Presences Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: United Nations (UN) The Strategy and Plan of Action acknowledges that hate speech has the potential to incite violence and undermine social unity. It recognizes that hate speech has been a precursor to atrocity crimes, including genocide, over the past 75 years. This approach to coordinating efforts across the UN system to identify, prevent and confront hate speech is grounded in international human rights standards, including the right to freedom of opinion and expression, principles of equality and non-discrimination, as well as other fundamental rights. The Strategy aims to give the United Nations the room and the resources to address hate speech, which poses a threat to UN principles, values and programmes. It guides the UN system on how to address hate speech and includes ways to support United Nations Resident Coordinators’ action in addressing and countering hate speech on the ground. 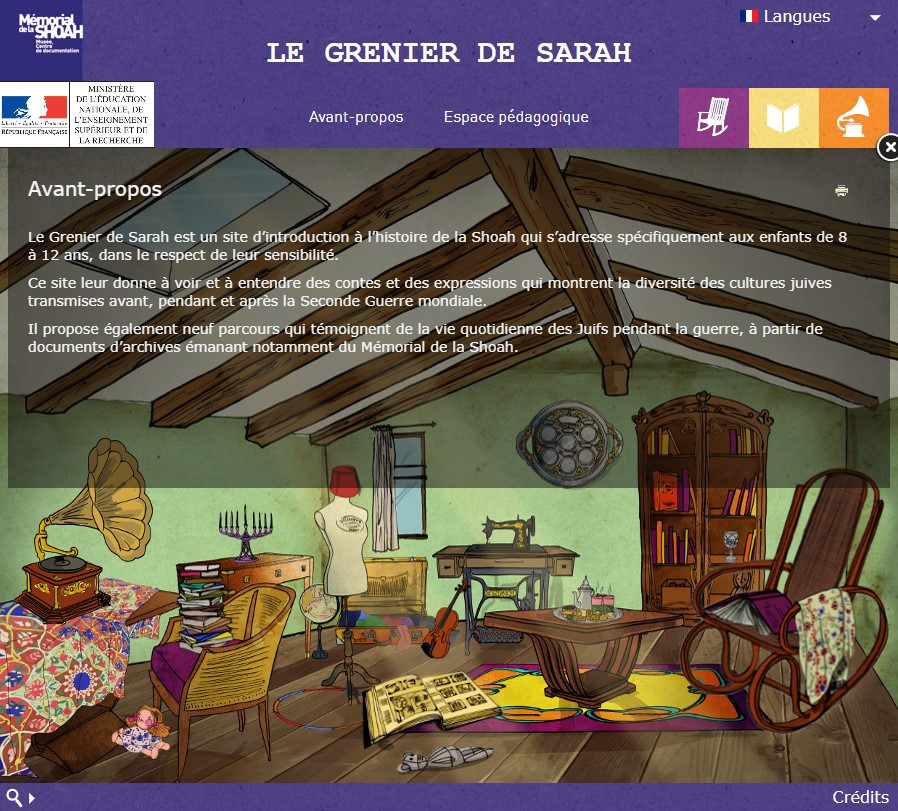 Le grenier de Sarah Author: Jacques Fredj | Barbara Mellul | Adeline Salmon | Barbara Mellul | Adeline Salmon | Tralalère | Alliance concept | Judith Panijel | Alban Perrin | Iannis Roder Lior Lalieu-Smadja | Karen Taieb | Ariel Sion Corporate author: Memorial de la Shoah Le Grenier de Sarah est un site d’introduction à l’histoire de la Shoah, créé spécifiquement pour les enfants de 8 à 12 ans, dans le respect de la sensibilité des jeunes visiteurs. Les choix éditoriaux et iconographiques du site traduisent scrupuleusement cette volonté de ne pas les choquer. Le site a été conçu à partir du questionnement des enfants sur cette période.- Qui étaient ces personnes que les nazis ont voulu assassiner ?- Dans quels pays vivaient-elles ? Quelles langues parlaient-elles ?- Quels ont été les parcours propres à chacune d’entre-elles ?Le Grenier de Sarah permet aux enfants de naviguer sur le site de façon autonome. Toutefois, il est conseillé aux adultes de les accompagner lors de leur première visite afin d’instaurer un dialogue et de répondre à d’éventuelles questions.Pour y répondre, trois rubriques, « Il était une fois », « Des mots à l’oreille » et « En noir et blanc », donnent des clefs de compréhension.- Dans « Il était une fois », des contes donnent un aperçu de la diversité des cultures juives. - Dans « Des mots à l’oreille », des expressions en hébreu, yiddish, judéo-espagnol et judéo-arabe ouvrent une fenêtre sur la pluralité du judaïsme. - Dans « En noir en blanc », neuf parcours témoignent de la vie quotidienne des Juifs pendant la guerre. En cliquant sur l’album photo, l’enfant choisit d’entendre un des récits de vie proposés.Tout au long de chaque parcours, des définitions et des documents, sont à la disposition du jeune visiteur. Pour les enseignants, un espace pédagogique spécifique a été créé afin d’y trouver des ressources complémentaires et des pistes de travail. Sarah’s attic is a website introducing to the Shoah History. It was specifically created for children from age 8 to 12 and respects their sensibility as young visitors. The contents and iconography are carefully intended to suit their emotional and cognitive abilities.The website was designed and elaborated from questions asked by children in History classes teaching this time period - Who were these persons the Nazis wanted to murder?- In which countries did they live? Which languages did they speak?- What were their personal experiences? Sarah’s attic enables children to navigate through the website on their own. Nevertheless, we recommend that adults accompany them on their first visit in order to create a dialog and answer possible questions.As part of a school or extra-curricular framework, this program can be used in small groups with the guidance of an adult.In order to answer these questions, three sections “Once upon a time”, “Words to my ear” and “In black and white” give keys to understanding the event.- In “Once upon a time”, tales give a glimpse of the diversity of Jewish cultures. - In “Words to my ear”, expressions in Hebrew, Yiddish, Judeo-Spanish and Judeo-Arabic open a window on the pluralism of Judaism. - In “In Black and white”, nine personal itineraries bear witness of the daily life of Jews during the war. Along each personal story, definitions and documents are available to the young visitor.For teachers and educators, a specific educational section contains additional resources, guidelines and teaching materials.
Le grenier de Sarah Author: Jacques Fredj | Barbara Mellul | Adeline Salmon | Barbara Mellul | Adeline Salmon | Tralalère | Alliance concept | Judith Panijel | Alban Perrin | Iannis Roder Lior Lalieu-Smadja | Karen Taieb | Ariel Sion Corporate author: Memorial de la Shoah Le Grenier de Sarah est un site d’introduction à l’histoire de la Shoah, créé spécifiquement pour les enfants de 8 à 12 ans, dans le respect de la sensibilité des jeunes visiteurs. Les choix éditoriaux et iconographiques du site traduisent scrupuleusement cette volonté de ne pas les choquer. Le site a été conçu à partir du questionnement des enfants sur cette période.- Qui étaient ces personnes que les nazis ont voulu assassiner ?- Dans quels pays vivaient-elles ? Quelles langues parlaient-elles ?- Quels ont été les parcours propres à chacune d’entre-elles ?Le Grenier de Sarah permet aux enfants de naviguer sur le site de façon autonome. Toutefois, il est conseillé aux adultes de les accompagner lors de leur première visite afin d’instaurer un dialogue et de répondre à d’éventuelles questions.Pour y répondre, trois rubriques, « Il était une fois », « Des mots à l’oreille » et « En noir et blanc », donnent des clefs de compréhension.- Dans « Il était une fois », des contes donnent un aperçu de la diversité des cultures juives. - Dans « Des mots à l’oreille », des expressions en hébreu, yiddish, judéo-espagnol et judéo-arabe ouvrent une fenêtre sur la pluralité du judaïsme. - Dans « En noir en blanc », neuf parcours témoignent de la vie quotidienne des Juifs pendant la guerre. En cliquant sur l’album photo, l’enfant choisit d’entendre un des récits de vie proposés.Tout au long de chaque parcours, des définitions et des documents, sont à la disposition du jeune visiteur. Pour les enseignants, un espace pédagogique spécifique a été créé afin d’y trouver des ressources complémentaires et des pistes de travail. Sarah’s attic is a website introducing to the Shoah History. It was specifically created for children from age 8 to 12 and respects their sensibility as young visitors. The contents and iconography are carefully intended to suit their emotional and cognitive abilities.The website was designed and elaborated from questions asked by children in History classes teaching this time period - Who were these persons the Nazis wanted to murder?- In which countries did they live? Which languages did they speak?- What were their personal experiences? Sarah’s attic enables children to navigate through the website on their own. Nevertheless, we recommend that adults accompany them on their first visit in order to create a dialog and answer possible questions.As part of a school or extra-curricular framework, this program can be used in small groups with the guidance of an adult.In order to answer these questions, three sections “Once upon a time”, “Words to my ear” and “In black and white” give keys to understanding the event.- In “Once upon a time”, tales give a glimpse of the diversity of Jewish cultures. - In “Words to my ear”, expressions in Hebrew, Yiddish, Judeo-Spanish and Judeo-Arabic open a window on the pluralism of Judaism. - In “In Black and white”, nine personal itineraries bear witness of the daily life of Jews during the war. Along each personal story, definitions and documents are available to the young visitor.For teachers and educators, a specific educational section contains additional resources, guidelines and teaching materials.  New Challenges and Approaches to Regional and Global Security in Central Asia Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) On 26 October 2018 in Nur-Sultan, the OSCE Programme Office in Nur-Sultan jointly with the Friedrich Ebert Foundation and the Kazakhstan Council on International Relations, with support from the Institute of Diplomacy under the Academy of Public Administration and the Public Opinion Research Institute co-organized an international conference entitled “New Challenges and Approaches to Regional and Global Security in Central Asia”. This compendium, which includes presentations given at the conference by both Kazakhstan’s and foreign participants, explores main regional security threats in Central Asia and ways to address these problems, as well as regional co-operation issues in responding to contemporary challenges. The edition will be of interest to political scientists, international relations experts, civil servants, scholars, educators, university-level students, and broad sections of the public interested in the contemporary development of the region. The edition is published in Russian and English. The paper of Mr. Pal Dunay is written in the English language in the original, the rest of the reports are in Russian. All reports have been translated and edited with the support of the OSCE Program Office in Nur Sultan. Any opinions and recommendations expressed in the materials arising from the conference are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the conference organizers.
New Challenges and Approaches to Regional and Global Security in Central Asia Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) On 26 October 2018 in Nur-Sultan, the OSCE Programme Office in Nur-Sultan jointly with the Friedrich Ebert Foundation and the Kazakhstan Council on International Relations, with support from the Institute of Diplomacy under the Academy of Public Administration and the Public Opinion Research Institute co-organized an international conference entitled “New Challenges and Approaches to Regional and Global Security in Central Asia”. This compendium, which includes presentations given at the conference by both Kazakhstan’s and foreign participants, explores main regional security threats in Central Asia and ways to address these problems, as well as regional co-operation issues in responding to contemporary challenges. The edition will be of interest to political scientists, international relations experts, civil servants, scholars, educators, university-level students, and broad sections of the public interested in the contemporary development of the region. The edition is published in Russian and English. The paper of Mr. Pal Dunay is written in the English language in the original, the rest of the reports are in Russian. All reports have been translated and edited with the support of the OSCE Program Office in Nur Sultan. Any opinions and recommendations expressed in the materials arising from the conference are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the conference organizers.  Новые вызовы и подходы по регионально и глобальной безопасности в Центральной Азии Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) 26 октября 2018 г. Офисом программ ОБСЕ в Нур-Султане совместно с Фондом им. Фридриха Эберта и Казахстанским советом по международным отношениям при поддержке Института дипломатии Академии государственного управления и Исследовательского института «Общественное мнение» была организована международная конференция «Новые вызовы и подходы по регионально и глобальной безопасности в Центральной Азии». В данный сборник материалов включены доклады казахстанских и зарубежных участников конференции, раскрывающие основные угрозы безопасности в регионе Центральной Азии и пути решения возникающих проблем, а также актуальные вопросы регионального сотрудничества в реагировании на современные вызовы. Издание предназначено для политологов, экспертов-международников, государственных служащих, научных работников, преподавателей и студентов высших учебных заведений, а также для широкого круга читателей, интересующихся современным развитием региона. Издание публикуется на русском и английском языках. Доклад господина Пал Дунай написан на английском языке в оригинале, остальные доклады на русском языке. Все доклады переведены и отредактированы при содействии Офиса программ ОБСЕ в Нур-Султане. Мнения и рекомендации авторов докладов в рамках конференции принадлежат авторам и не обязательно отражают точку зрения организаторов конференции.
Новые вызовы и подходы по регионально и глобальной безопасности в Центральной Азии Year of publication: 2020 Corporate author: Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) 26 октября 2018 г. Офисом программ ОБСЕ в Нур-Султане совместно с Фондом им. Фридриха Эберта и Казахстанским советом по международным отношениям при поддержке Института дипломатии Академии государственного управления и Исследовательского института «Общественное мнение» была организована международная конференция «Новые вызовы и подходы по регионально и глобальной безопасности в Центральной Азии». В данный сборник материалов включены доклады казахстанских и зарубежных участников конференции, раскрывающие основные угрозы безопасности в регионе Центральной Азии и пути решения возникающих проблем, а также актуальные вопросы регионального сотрудничества в реагировании на современные вызовы. Издание предназначено для политологов, экспертов-международников, государственных служащих, научных работников, преподавателей и студентов высших учебных заведений, а также для широкого круга читателей, интересующихся современным развитием региона. Издание публикуется на русском и английском языках. Доклад господина Пал Дунай написан на английском языке в оригинале, остальные доклады на русском языке. Все доклады переведены и отредактированы при содействии Офиса программ ОБСЕ в Нур-Султане. Мнения и рекомендации авторов докладов в рамках конференции принадлежат авторам и не обязательно отражают точку зрения организаторов конференции.  Colloquium Report: Building Resilience to Genocide through Peace Education: Concepts, Methods, Tools and Impact Year of publication: 2017 Author: Jonathan Bower, Mariana Goetz Corporate author: Aegis Trust A three-day Colloquium in Kigali in February brought together academics and practitioners in and around the field of peace education to share concepts, methods and means of measuring impact, contributing to a stronger evidence base for the effectiveness of peace education. Three interesting takeaways from the Colloquium: 1. Building resilience against genocide requires critical thinking about the process of identity-based violence and its reversal.2. The content of peace education programmes matters: interactive role-play type activities have been shown to have a longer lasting impact.3. Unhealed wounds need to be addressed to prevent a repeat of violence; psychosocial support must accompany peace education to reduce anxiety, which can be an obstacle when accessing empathy. A major achievement resulting from the consortium’s advocacy has been that the Government of Rwanda through the Ministry of Education has integrated Peace and Values education into the school curriculum. In a new phase of work Aegis is now supporting the implementation of the revised national curriculum that has integrated peace and values education (2016-19).
Colloquium Report: Building Resilience to Genocide through Peace Education: Concepts, Methods, Tools and Impact Year of publication: 2017 Author: Jonathan Bower, Mariana Goetz Corporate author: Aegis Trust A three-day Colloquium in Kigali in February brought together academics and practitioners in and around the field of peace education to share concepts, methods and means of measuring impact, contributing to a stronger evidence base for the effectiveness of peace education. Three interesting takeaways from the Colloquium: 1. Building resilience against genocide requires critical thinking about the process of identity-based violence and its reversal.2. The content of peace education programmes matters: interactive role-play type activities have been shown to have a longer lasting impact.3. Unhealed wounds need to be addressed to prevent a repeat of violence; psychosocial support must accompany peace education to reduce anxiety, which can be an obstacle when accessing empathy. A major achievement resulting from the consortium’s advocacy has been that the Government of Rwanda through the Ministry of Education has integrated Peace and Values education into the school curriculum. In a new phase of work Aegis is now supporting the implementation of the revised national curriculum that has integrated peace and values education (2016-19). 