Recursos
Exploren una amplia gama de recursos valiosos en GCED para profundizar su comprensión y promover su búsqueda, incidencia, enseñanza y aprendizaje.
125 resultados encontrados
 Women Key Actors of Food Resilience: A Reconfiguration of Gender Relations in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic Año de publicación: 2021 Autor corporativo: Centre for International Cooperation and Study (CECI) The Covid-19 pandemic and its response measures have intensified the vulnerability and shortcomings of food systems in West Africa, affecting all activities and processes of production, distribution, and consumption of food. To this end, rural women in Senegal and Burkina Faso, ensured the resilience of poor and vulnerable households, thus generating recognition of this reality by men. It is therefore essential to give women decision-making power at all levels in the spheres related to the four pillars of security eating. It would be desirable to support and accompany the positive reconfiguration of relationships of power between women and men, already in progress in the communities studied, to ensure that they have the means and skills (social, cultural, economic, political, and legal) to be able to fully play this role. Support for farmer organizations and networks of women's organizations is essential.
Women Key Actors of Food Resilience: A Reconfiguration of Gender Relations in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic Año de publicación: 2021 Autor corporativo: Centre for International Cooperation and Study (CECI) The Covid-19 pandemic and its response measures have intensified the vulnerability and shortcomings of food systems in West Africa, affecting all activities and processes of production, distribution, and consumption of food. To this end, rural women in Senegal and Burkina Faso, ensured the resilience of poor and vulnerable households, thus generating recognition of this reality by men. It is therefore essential to give women decision-making power at all levels in the spheres related to the four pillars of security eating. It would be desirable to support and accompany the positive reconfiguration of relationships of power between women and men, already in progress in the communities studied, to ensure that they have the means and skills (social, cultural, economic, political, and legal) to be able to fully play this role. Support for farmer organizations and networks of women's organizations is essential.  Les femmes actrices clés de résilience alimentaire: Une reconfiguration des rapports de genre en temps de pandémie de COVID-19 Año de publicación: 2021 Autor corporativo: Centre for International Cooperation and Study (CECI) La pandémie de la Covid-19 et ses mesures de riposte ont intensifié la vulnérabilité et les insuffisances des systèmes alimentaires en Afrique de l’Ouest, en affectant l'ensemble des activités et des processus de production, de distribution et de consommation d'aliments. A cet effet, les femmes rurales au Sénégal et au Burkina Faso, ont assuré la résilience des ménages pauvres et vulnérables, suscitant ainsi une reconnaissance de cette réalité par les hommes. Il est donc essentiel de donner aux femmes du pouvoir décisionnel à tous les niveaux dans les sphères liées aux quatre (4) piliers de la sécurité alimentaire. Il serait souhaitable de soutenir et d’accompagner la reconfiguration positive des rapports de pouvoir entre les femmes et les hommes, déjà en cours dans les communautés étudiées, afin d'assurer qu'elles aient les moyens et habilités (sociales, culturelles, économiques, politiques et juridiques) pour pouvoir jouer pleinement ce rôle. Un appui aux organisations paysannes et aux réseaux d’organisations de femmes est essentiel.
Les femmes actrices clés de résilience alimentaire: Une reconfiguration des rapports de genre en temps de pandémie de COVID-19 Año de publicación: 2021 Autor corporativo: Centre for International Cooperation and Study (CECI) La pandémie de la Covid-19 et ses mesures de riposte ont intensifié la vulnérabilité et les insuffisances des systèmes alimentaires en Afrique de l’Ouest, en affectant l'ensemble des activités et des processus de production, de distribution et de consommation d'aliments. A cet effet, les femmes rurales au Sénégal et au Burkina Faso, ont assuré la résilience des ménages pauvres et vulnérables, suscitant ainsi une reconnaissance de cette réalité par les hommes. Il est donc essentiel de donner aux femmes du pouvoir décisionnel à tous les niveaux dans les sphères liées aux quatre (4) piliers de la sécurité alimentaire. Il serait souhaitable de soutenir et d’accompagner la reconfiguration positive des rapports de pouvoir entre les femmes et les hommes, déjà en cours dans les communautés étudiées, afin d'assurer qu'elles aient les moyens et habilités (sociales, culturelles, économiques, politiques et juridiques) pour pouvoir jouer pleinement ce rôle. Un appui aux organisations paysannes et aux réseaux d’organisations de femmes est essentiel. 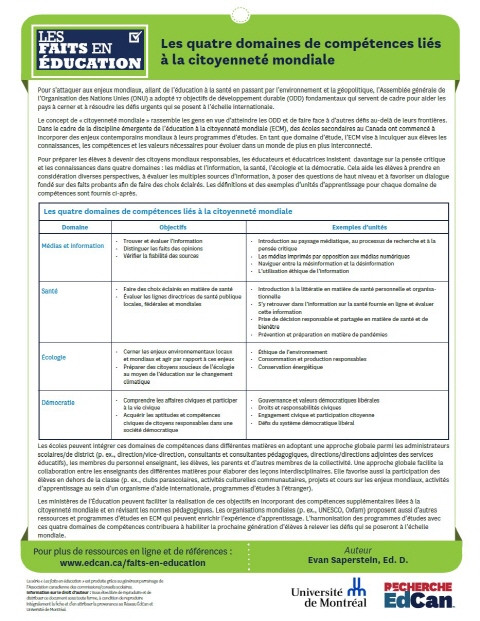 The Four Areas of Competence Linked to Global Citizenship Año de publicación: 2023 Autor: Evan Saperstein Autor corporativo: Université de Montréal | Association Canadienne d'Education Ce document présente les quatre domaines de compétences liées à la citoyenneté, et comment les intégrer à l'éducation des élèves. Pour préparer les élèves à devenir des citoyens mondiaux responsables, les éducateurs et éducatrices insistent davantage sur la pensée critique et les connaissances dans quatre domaines : les médias et l’information, la santé, l’écologie et la démocratie. This document presents the four areas of competency linked to citizenship, and how to integrate them into pupils' education. To prepare students to become responsible global citizens, educators are placing greater emphasis on critical thinking and knowledge in four areas: media and information, health, ecology and democracy.
The Four Areas of Competence Linked to Global Citizenship Año de publicación: 2023 Autor: Evan Saperstein Autor corporativo: Université de Montréal | Association Canadienne d'Education Ce document présente les quatre domaines de compétences liées à la citoyenneté, et comment les intégrer à l'éducation des élèves. Pour préparer les élèves à devenir des citoyens mondiaux responsables, les éducateurs et éducatrices insistent davantage sur la pensée critique et les connaissances dans quatre domaines : les médias et l’information, la santé, l’écologie et la démocratie. This document presents the four areas of competency linked to citizenship, and how to integrate them into pupils' education. To prepare students to become responsible global citizens, educators are placing greater emphasis on critical thinking and knowledge in four areas: media and information, health, ecology and democracy.  Les quatre domaines de compétences liés à la citoyenneté mondiale Año de publicación: 2023 Autor: Evan Saperstein Autor corporativo: Université de Montréal | Association Canadienne d'Education Ce document présente les quatre domaines de compétences liées à la citoyenneté, et comment les intégrer à l'éducation des élèves. Pour préparer les élèves à devenir des citoyens mondiaux responsables, les éducateurs et éducatrices insistent davantage sur la pensée critique et les connaissances dans quatre domaines : les médias et l’information, la santé, l’écologie et la démocratie. This document presents the four areas of competency linked to citizenship, and how to integrate them into pupils' education. To prepare students to become responsible global citizens, educators are placing greater emphasis on critical thinking and knowledge in four areas: media and information, health, ecology and democracy.
Les quatre domaines de compétences liés à la citoyenneté mondiale Año de publicación: 2023 Autor: Evan Saperstein Autor corporativo: Université de Montréal | Association Canadienne d'Education Ce document présente les quatre domaines de compétences liées à la citoyenneté, et comment les intégrer à l'éducation des élèves. Pour préparer les élèves à devenir des citoyens mondiaux responsables, les éducateurs et éducatrices insistent davantage sur la pensée critique et les connaissances dans quatre domaines : les médias et l’information, la santé, l’écologie et la démocratie. This document presents the four areas of competency linked to citizenship, and how to integrate them into pupils' education. To prepare students to become responsible global citizens, educators are placing greater emphasis on critical thinking and knowledge in four areas: media and information, health, ecology and democracy.  SDG 4 Data Digest 2018: Data to Nurture Learning Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) The world is facing a crisis of learning, with many children leaving school without the basic skills they need for a prosperous and productive adult life. Two-thirds of the estimated 617 million children and adolescents who cannot read a simple sentence or manage a basic mathematics calculation are in the classroom. Too many are waiting for a quality education that never comes.As the 2018 SDG 4 Data Digest shows, it is not enough to hope that they will stay in school and somehow acquire skills in reading and mathematics. It is critical to monitor those skills as children progress through school. That requires comparable data, over time, to ensure that children – and the education systems that serve them – are on track.Given the critical importance of learning for the achievement of all the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), from poverty reduction to peaceful societies, this year’s edition of the SDG 4 Data Digest is dedicated to the theme of learning outcomes. It showcases the most comprehensive and up-to-date compilation of work to inform the learning indicators of SDG 4.The Digest discusses learning evidence on early child development, mathematics and reading skills among school-aged children, and digital and work-related skills among youth and adults. It highlights the conceptual frameworks and tools developed by leading authors and institutions to understand, measure, monitor and support learning for all. It also considers the implications of reporting for SDG 4.
SDG 4 Data Digest 2018: Data to Nurture Learning Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) The world is facing a crisis of learning, with many children leaving school without the basic skills they need for a prosperous and productive adult life. Two-thirds of the estimated 617 million children and adolescents who cannot read a simple sentence or manage a basic mathematics calculation are in the classroom. Too many are waiting for a quality education that never comes.As the 2018 SDG 4 Data Digest shows, it is not enough to hope that they will stay in school and somehow acquire skills in reading and mathematics. It is critical to monitor those skills as children progress through school. That requires comparable data, over time, to ensure that children – and the education systems that serve them – are on track.Given the critical importance of learning for the achievement of all the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), from poverty reduction to peaceful societies, this year’s edition of the SDG 4 Data Digest is dedicated to the theme of learning outcomes. It showcases the most comprehensive and up-to-date compilation of work to inform the learning indicators of SDG 4.The Digest discusses learning evidence on early child development, mathematics and reading skills among school-aged children, and digital and work-related skills among youth and adults. It highlights the conceptual frameworks and tools developed by leading authors and institutions to understand, measure, monitor and support learning for all. It also considers the implications of reporting for SDG 4.  ЦУР 4 Дайджест данных 2018: данные для обучения Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) Мир сталкивается с кризисом обучения, когда многие дети покидают школу без базовых навыков, необходимых для процветающей и продуктивной взрослой жизни. Две трети из примерно 617 миллионов детей и подростков, посещающих школу, не могут прочитать простое предложение или произвести элементарные математические вычисления. При этом качественное образование для очень многих продолжает оставаться недоступным.Как показывает Дайджест данных ЦУР 4 2018 года, недостаточно просто надеяться, что они, оставаясь в школе, каким-то образом приобретут навыки чтения и математики. Очень важно следить за развитием этих навыков по мере того, как дети учатся в школе. Сопоставление данных с течением времени является необходимым фактором, гарантирующим, что дети и системы образования, которые их обслуживают, находятся на правильном пути.Учитывая исключительную важность обучения для достижения всех Целей в области устойчивого развития (ЦУР), от сокращения бедности до мирных обществ, выпуск Дайджеста данных ЦУР 4 в этом году посвящен теме результатов обучения. Он демонстрирует наиболее полную и актуальную подборку работ для информирования об учебных показателях ЦУР 4.В Дайджесте обсуждаются фактические данные о раннем развитии детей, математике и навыках чтения среди детей школьного возраста, а также трудовые навыки и навыки работы с цифровыми технологиями среди молодежи и взрослых. В нем освещаются концептуальные основы и инструменты, разработанные ведущими авторами и учреждениями для понимания, измерения, мониторинга и поддержки обучения для всех. В нем также рассматриваются результаты отчетности для ЦУР 4.
ЦУР 4 Дайджест данных 2018: данные для обучения Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) Мир сталкивается с кризисом обучения, когда многие дети покидают школу без базовых навыков, необходимых для процветающей и продуктивной взрослой жизни. Две трети из примерно 617 миллионов детей и подростков, посещающих школу, не могут прочитать простое предложение или произвести элементарные математические вычисления. При этом качественное образование для очень многих продолжает оставаться недоступным.Как показывает Дайджест данных ЦУР 4 2018 года, недостаточно просто надеяться, что они, оставаясь в школе, каким-то образом приобретут навыки чтения и математики. Очень важно следить за развитием этих навыков по мере того, как дети учатся в школе. Сопоставление данных с течением времени является необходимым фактором, гарантирующим, что дети и системы образования, которые их обслуживают, находятся на правильном пути.Учитывая исключительную важность обучения для достижения всех Целей в области устойчивого развития (ЦУР), от сокращения бедности до мирных обществ, выпуск Дайджеста данных ЦУР 4 в этом году посвящен теме результатов обучения. Он демонстрирует наиболее полную и актуальную подборку работ для информирования об учебных показателях ЦУР 4.В Дайджесте обсуждаются фактические данные о раннем развитии детей, математике и навыках чтения среди детей школьного возраста, а также трудовые навыки и навыки работы с цифровыми технологиями среди молодежи и взрослых. В нем освещаются концептуальные основы и инструменты, разработанные ведущими авторами и учреждениями для понимания, измерения, мониторинга и поддержки обучения для всех. В нем также рассматриваются результаты отчетности для ЦУР 4.  SDG 4 Data Book: Global Education Indicators 2018 Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) This publication presents the global monitoring indicators used by countries and the international development community to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) on education. The indicators were produced by the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS), based on the latest available data.The UIS is the official source of internationally-comparable education data and the custodian agency for SDG 4 data.This mandate reflects the trust of the international community in UIS data and its proven track record in methodological work and standard-setting with national statistical offices, line ministries and technical partners in every region.This publication presents a snapshot of the data used to monitor progress towards the global education goal and targets. It complements the UIS Quick Guide to Education Indicators for SDG 4, which provides more detailed information on the development, interpretation and use of the indicators.
SDG 4 Data Book: Global Education Indicators 2018 Año de publicación: 2018 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) This publication presents the global monitoring indicators used by countries and the international development community to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) on education. The indicators were produced by the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS), based on the latest available data.The UIS is the official source of internationally-comparable education data and the custodian agency for SDG 4 data.This mandate reflects the trust of the international community in UIS data and its proven track record in methodological work and standard-setting with national statistical offices, line ministries and technical partners in every region.This publication presents a snapshot of the data used to monitor progress towards the global education goal and targets. It complements the UIS Quick Guide to Education Indicators for SDG 4, which provides more detailed information on the development, interpretation and use of the indicators.  SDG 4 Data Digest: How to Produce and Use the Global and Thematic Education Indicators Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) This edition of the SDG 4 Data Digest from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) aims to help countries develop and report the indicators needed to deliver on the promise of Sustainable Development Goal 4 – a quality education for all by 2030.It stresses the urgency: every child in the generation that should finish secondary education by the deadline should be in a primary classroom right now. Yet if current trends continue, and without a rapid shift from “business as usual”, one in six children aged 6 to 17 will still be out of school in 2030 while just six in ten youth will be completing secondary education. Moreover, there is an urgent need to improve the quality of education on offer. According to UIS estimates, 55% of children and adolescents of primary and lower secondary school age are not achieving minimum proficiency levels in reading and 60% are not acquiring critical skills in mathematics The investment case for education is clear and has been repeated time and time again: education reduces poverty, improves health and nutrition, advances equity and drives national prosperity. But education systems cannot function effectively without a clear picture of progress – or the lack of it – and without knowing who is missing out on education and why.To help ll such gaps, the Digest focuses on new methodologies to help countries build a full and accurate understanding of their own education successes and challenges while generating the internationally comparable data needed for global monitoring. Through these methodological tools, countries can track and accelerate progress on their own education priorities and contribute to the global achievement of SDG4.
SDG 4 Data Digest: How to Produce and Use the Global and Thematic Education Indicators Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) This edition of the SDG 4 Data Digest from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) aims to help countries develop and report the indicators needed to deliver on the promise of Sustainable Development Goal 4 – a quality education for all by 2030.It stresses the urgency: every child in the generation that should finish secondary education by the deadline should be in a primary classroom right now. Yet if current trends continue, and without a rapid shift from “business as usual”, one in six children aged 6 to 17 will still be out of school in 2030 while just six in ten youth will be completing secondary education. Moreover, there is an urgent need to improve the quality of education on offer. According to UIS estimates, 55% of children and adolescents of primary and lower secondary school age are not achieving minimum proficiency levels in reading and 60% are not acquiring critical skills in mathematics The investment case for education is clear and has been repeated time and time again: education reduces poverty, improves health and nutrition, advances equity and drives national prosperity. But education systems cannot function effectively without a clear picture of progress – or the lack of it – and without knowing who is missing out on education and why.To help ll such gaps, the Digest focuses on new methodologies to help countries build a full and accurate understanding of their own education successes and challenges while generating the internationally comparable data needed for global monitoring. Through these methodological tools, countries can track and accelerate progress on their own education priorities and contribute to the global achievement of SDG4.  Compendio de Datos sobre el ODS 4: Cómo producir y utilizar los indicadores globales y temáticos sobre educación Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) La presente edición del Compendio de Datos ODS 4 publicada por el Instituto de Estadística de la UNESCO (UIS) pretende a ayudar a los países a desarrollar y reportar los indicadores que se requerirán para cumplir la promesa del Objetivo de Desarrollo Sostenible 4 – una educación de calidad para todos de aquí al 2030. Se pone énfasis en la urgencia: todo niño que forma parte de la generación que debería concluir la educación secundaria dentro del plazo, debería estar en un aula de primaria hoy. Sin embargo, si la actual tendencia continúa, y de no mediar un drástico cambio, uno de cada seis niños entre 6 y 17 años aún estará fuera de la escuela en 2030 y solo seis de cada diez jóvenes habrán completado su educación secundaria. Adicionalmente, existe la urgente necesidad de mejorar la calidad de la educación que hoy se ofrece. De acuerdo con estimaciones del UIS, el 55% de los niños y adolescentes en edad de cursar educación primaria y educación secundaria baja no están adquiriendo niveles mínimos de competencia en lectura y 60% no está adquiriendo competencias fundamentales en matemáticas. El caso de inversión para la educación es claro y se ha repetido una y otra vez: la educación reduce la pobreza, mejora la salud y la nutrición, promueve la equidad y fomenta la prosperidad nacional. Sin embargo, los sistemas educativos no pueden funcionar en forma eficiente si no cuentan con un escenario claro - o con ningún escenario - del avance y sin saber quién no está recibiendo educación y por qué. Para ayudar a cerrar estas brechas, el Compendio se centra en nuevas metodologías que ayudan a los países a desarrollar una clara y completa visión de sus propios éxitos y desafíos en materia de educación, al tiempo que genera los datos internacionalmente comparables necesarios para el monitoreo global. A través de estas herramientas metodológicas, los países podrán rastrear y acelerar el avance de sus propias prioridades de educación y contribuir al logro global del ODS 4.
Compendio de Datos sobre el ODS 4: Cómo producir y utilizar los indicadores globales y temáticos sobre educación Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) La presente edición del Compendio de Datos ODS 4 publicada por el Instituto de Estadística de la UNESCO (UIS) pretende a ayudar a los países a desarrollar y reportar los indicadores que se requerirán para cumplir la promesa del Objetivo de Desarrollo Sostenible 4 – una educación de calidad para todos de aquí al 2030. Se pone énfasis en la urgencia: todo niño que forma parte de la generación que debería concluir la educación secundaria dentro del plazo, debería estar en un aula de primaria hoy. Sin embargo, si la actual tendencia continúa, y de no mediar un drástico cambio, uno de cada seis niños entre 6 y 17 años aún estará fuera de la escuela en 2030 y solo seis de cada diez jóvenes habrán completado su educación secundaria. Adicionalmente, existe la urgente necesidad de mejorar la calidad de la educación que hoy se ofrece. De acuerdo con estimaciones del UIS, el 55% de los niños y adolescentes en edad de cursar educación primaria y educación secundaria baja no están adquiriendo niveles mínimos de competencia en lectura y 60% no está adquiriendo competencias fundamentales en matemáticas. El caso de inversión para la educación es claro y se ha repetido una y otra vez: la educación reduce la pobreza, mejora la salud y la nutrición, promueve la equidad y fomenta la prosperidad nacional. Sin embargo, los sistemas educativos no pueden funcionar en forma eficiente si no cuentan con un escenario claro - o con ningún escenario - del avance y sin saber quién no está recibiendo educación y por qué. Para ayudar a cerrar estas brechas, el Compendio se centra en nuevas metodologías que ayudan a los países a desarrollar una clara y completa visión de sus propios éxitos y desafíos en materia de educación, al tiempo que genera los datos internacionalmente comparables necesarios para el monitoreo global. A través de estas herramientas metodológicas, los países podrán rastrear y acelerar el avance de sus propias prioridades de educación y contribuir al logro global del ODS 4.  Rapport sur les données de l’ODD 4: Comment produire et utiliser les indicateurs mondiaux et thématiques de l’éducation Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) La présente édition du Rapport sur les données de l’ODD 4 de l’Institut de statistique de l’UNESCO (ISU) vise à aider les pays à élaborer et à fournir les indicateurs nécessaires pour respecter la promesse de l’Objectif de développement durable 4 (ODD 4) : assurer l’accès de tous à une éducation de qualité d’ici 2030. Il insiste sur l’urgence que chaque enfant de la génération qui doit achever le cycle secondaire à l’échéance 2030 soit inscrit dans le primaire dès aujourd’hui. Cependant, si la tendance actuelle et le statu quo se poursuivent, un enfant de 6 à 17 ans sur six ne sera toujours pas scolarisé en 2030, et seuls six jeunes sur dix achèveront le cycle secondaire. Par ailleurs, il est urgent d’améliorer la qualité de l’éducation offerte. Selon les estimations de l’ISU, 55 % des enfants et des adolescents en âge de fréquenter le primaire et le premier cycle du secondaire n’atteignent pas les seuils minimaux de compétence en lecture, et 60 % n’acquièrent pas ces seuils en mathématiques. Les arguments en faveur de l’investissement dans l’éducation sont clairs et ont été répétés à maintes reprises : l’éducation réduit la pauvreté, améliore la santé et la nutrition, fait avancer l’équité et stimule la prospérité nationale. Mais les systèmes éducatifs ne peuvent pas fonctionner efficacement s’ils ne disposent pas du tableau des progrès accomplis – ou de leur absence – et sans savoir ce dont manque l’éducation et pourquoi. Pour contribuer à combler ces lacunes, le Rapport se concentre sur les nouvelles méthodologies pour aider les pays à développer une compréhension précise de leurs progrès, de leurs succès et de leurs défis dans le domaine de l’éducation, tout en produisant des données comparables sur le plan international pour le suivi mondial. Ces outils méthodologiques leur donneront les moyens de suivre et d’accélérer les progrès accomplis pour atteindre leurs propres priorités éducatives et contribuer à la réalisation de l’ODD 4.
Rapport sur les données de l’ODD 4: Comment produire et utiliser les indicateurs mondiaux et thématiques de l’éducation Año de publicación: 2019 Autor corporativo: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) La présente édition du Rapport sur les données de l’ODD 4 de l’Institut de statistique de l’UNESCO (ISU) vise à aider les pays à élaborer et à fournir les indicateurs nécessaires pour respecter la promesse de l’Objectif de développement durable 4 (ODD 4) : assurer l’accès de tous à une éducation de qualité d’ici 2030. Il insiste sur l’urgence que chaque enfant de la génération qui doit achever le cycle secondaire à l’échéance 2030 soit inscrit dans le primaire dès aujourd’hui. Cependant, si la tendance actuelle et le statu quo se poursuivent, un enfant de 6 à 17 ans sur six ne sera toujours pas scolarisé en 2030, et seuls six jeunes sur dix achèveront le cycle secondaire. Par ailleurs, il est urgent d’améliorer la qualité de l’éducation offerte. Selon les estimations de l’ISU, 55 % des enfants et des adolescents en âge de fréquenter le primaire et le premier cycle du secondaire n’atteignent pas les seuils minimaux de compétence en lecture, et 60 % n’acquièrent pas ces seuils en mathématiques. Les arguments en faveur de l’investissement dans l’éducation sont clairs et ont été répétés à maintes reprises : l’éducation réduit la pauvreté, améliore la santé et la nutrition, fait avancer l’équité et stimule la prospérité nationale. Mais les systèmes éducatifs ne peuvent pas fonctionner efficacement s’ils ne disposent pas du tableau des progrès accomplis – ou de leur absence – et sans savoir ce dont manque l’éducation et pourquoi. Pour contribuer à combler ces lacunes, le Rapport se concentre sur les nouvelles méthodologies pour aider les pays à développer une compréhension précise de leurs progrès, de leurs succès et de leurs défis dans le domaine de l’éducation, tout en produisant des données comparables sur le plan international pour le suivi mondial. Ces outils méthodologiques leur donneront les moyens de suivre et d’accélérer les progrès accomplis pour atteindre leurs propres priorités éducatives et contribuer à la réalisation de l’ODD 4. 