相关资源
探索丰富的全球公民教育资源,深化理解,促进研究、倡导、教学与学习。
共找到40条结果
 دروس عين الدراسات الاجتماعية والمواطنة– برنامج تعزيز الشخصية - سادس ابتدائي 出版年份: 2020 作者: Fawzia Alghamdi 机构作者: iEN National Education Portal تقوم المعلمة بشرح درس للصف السادس الابتدائي في تنمية وتعزيز الشخصية. الدرس لطلاب المملكة العربية السعودية في مقرر الدراسات الاجتماعية. لقد ظهرت الدروس التي تشرح عبر المنصات مع جائحة كورونا.
دروس عين الدراسات الاجتماعية والمواطنة– برنامج تعزيز الشخصية - سادس ابتدائي 出版年份: 2020 作者: Fawzia Alghamdi 机构作者: iEN National Education Portal تقوم المعلمة بشرح درس للصف السادس الابتدائي في تنمية وتعزيز الشخصية. الدرس لطلاب المملكة العربية السعودية في مقرر الدراسات الاجتماعية. لقد ظهرت الدروس التي تشرح عبر المنصات مع جائحة كورونا.  iEN Social Studies and Citizenship Lessons: Personality Enhancement Program - Sixth Primary 出版年份: 2020 作者: Fawzia Alghamdi 机构作者: iEN National Education Portal The teacher explains a sixth grade lesson on character development and enhancement. The lesson for students of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in a social studies course. With the Coronavirus pandemic, lessons explaining across platforms have emerged.
iEN Social Studies and Citizenship Lessons: Personality Enhancement Program - Sixth Primary 出版年份: 2020 作者: Fawzia Alghamdi 机构作者: iEN National Education Portal The teacher explains a sixth grade lesson on character development and enhancement. The lesson for students of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in a social studies course. With the Coronavirus pandemic, lessons explaining across platforms have emerged. 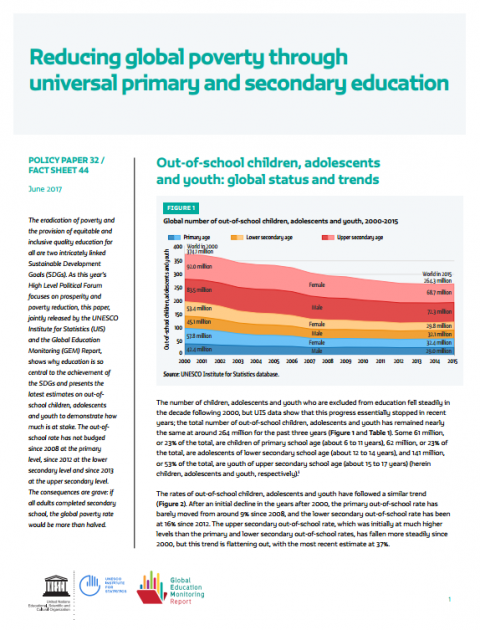 Reducing global poverty through universal primary and secondary education 出版年份: 2017 机构作者: UNESCO The eradication of poverty and the provision of equitable and inclusive quality education for all are two intricately linked Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As this year’s High Level Political Forum focuses on prosperity and poverty reduction, this paper, jointly released by the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) and the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report, shows why education is so central to the achievement of the SDGs and presents the latest estimates on out-ofschool children, adolescents and youth to demonstrate how much is at stake. The out-ofschool rate has not budged since 2008 at the primary level, since 2012 at the lower secondary level and since 2013 at the upper secondary level. The consequences are grave: if all adults completed secondary school, the global poverty rate would be more than halved.
Reducing global poverty through universal primary and secondary education 出版年份: 2017 机构作者: UNESCO The eradication of poverty and the provision of equitable and inclusive quality education for all are two intricately linked Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As this year’s High Level Political Forum focuses on prosperity and poverty reduction, this paper, jointly released by the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) and the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report, shows why education is so central to the achievement of the SDGs and presents the latest estimates on out-ofschool children, adolescents and youth to demonstrate how much is at stake. The out-ofschool rate has not budged since 2008 at the primary level, since 2012 at the lower secondary level and since 2013 at the upper secondary level. The consequences are grave: if all adults completed secondary school, the global poverty rate would be more than halved.  دور اللغة الأم في تعلم اللغة العربية الفصحى في المرحلة الابتدائية بالمدرسة الجزائرية 出版年份: 2012 作者: Khaled Abdel Salam 机构作者: Farhat Abbas Setif University تهدف دراستنا إلى التعرف على تأثيرات اللغة األولى سواء كانت عامية عربية او قبائلية في تعلم اللغة المدرسية في مختلف البنيات اللغوية الصوتية والمفرداتية والتركيبية والنحوية والصرفية. وبالتالي الكشف إن كانت ،عامال ميسرا في التعلم أو معرقال. و التعرف على االستراتيجيات المعرفية التي يستعملها المتعلمون في تعلمهم وعالقتها بأدائهم اللغوي في التعبيرين الشفوي والكتابي. ولتحقيق ذلك استعملنا المنهج الوصفي التحليلي، فاخترنا عينتين بمجموع 90 تلميذا (45 ناطقا بالعامية العربية و45 ناطقا بالقبائلية). فطبقنا عليهما ثالث اختبارات، أحدهما شفوي على شكل مقابلة حول معلومات شخصية وصحية واآلخر كتابي حول المحافظة على البيئة، ومقياس حول ،استراتيجيات التعلم. ولما حللنا محتوى االجابات واستخرجنا األخطاء اللغوية المنتشرة وصنفناها إلى مختلف األنماط وبعد حسابنا لتكراراتها و تحليلنا وتفسيرنا لها، توصلنا إلى النتائج اآلتية: ـ أن اللغة األولى سواء كانت عامية عربية او قبائلية قد أثرت بشكل كبير في كل بنيات اللغة الصوتية، التركيبية، النحوية والصرفية بشكل كبير حتى أصبحت .لغة التعليم ال تختلف كثيرا عنها. لذلك استنتجنا أنه ال يمكن اعتبارها عامال ميسرا في التعلم .ـ أن المتعلمين يستخدمون كثيرا استراتيجيات المراجعة للدروس واالستنباط أكثر من االستراتيجيات األخرى .ـ أنه ال توجد عالقة بين االستراتيجيات المستعملة وأداء المعلمين باللغة المدرسية شفويا وكتابيا ـ وأنها ال توجد فروق ذات داللة إحصائية بين الناطقين بالعامية العربية و الناطقين بالقبائلية في البنية الصوتية لكن هناك فروقا دالة إحصائيا بينهما في البنيتين النحوية والصرفية لكنها تعود إلى عوامل اخرى ذاتية وبيداغوجية .وأسرية .واستنتجنا ان مستوى المتعلمين من العينتين بلغة التعليم لم يرتق إلى الكفاءات المنشودة في المنهاج المدرسي.
دور اللغة الأم في تعلم اللغة العربية الفصحى في المرحلة الابتدائية بالمدرسة الجزائرية 出版年份: 2012 作者: Khaled Abdel Salam 机构作者: Farhat Abbas Setif University تهدف دراستنا إلى التعرف على تأثيرات اللغة األولى سواء كانت عامية عربية او قبائلية في تعلم اللغة المدرسية في مختلف البنيات اللغوية الصوتية والمفرداتية والتركيبية والنحوية والصرفية. وبالتالي الكشف إن كانت ،عامال ميسرا في التعلم أو معرقال. و التعرف على االستراتيجيات المعرفية التي يستعملها المتعلمون في تعلمهم وعالقتها بأدائهم اللغوي في التعبيرين الشفوي والكتابي. ولتحقيق ذلك استعملنا المنهج الوصفي التحليلي، فاخترنا عينتين بمجموع 90 تلميذا (45 ناطقا بالعامية العربية و45 ناطقا بالقبائلية). فطبقنا عليهما ثالث اختبارات، أحدهما شفوي على شكل مقابلة حول معلومات شخصية وصحية واآلخر كتابي حول المحافظة على البيئة، ومقياس حول ،استراتيجيات التعلم. ولما حللنا محتوى االجابات واستخرجنا األخطاء اللغوية المنتشرة وصنفناها إلى مختلف األنماط وبعد حسابنا لتكراراتها و تحليلنا وتفسيرنا لها، توصلنا إلى النتائج اآلتية: ـ أن اللغة األولى سواء كانت عامية عربية او قبائلية قد أثرت بشكل كبير في كل بنيات اللغة الصوتية، التركيبية، النحوية والصرفية بشكل كبير حتى أصبحت .لغة التعليم ال تختلف كثيرا عنها. لذلك استنتجنا أنه ال يمكن اعتبارها عامال ميسرا في التعلم .ـ أن المتعلمين يستخدمون كثيرا استراتيجيات المراجعة للدروس واالستنباط أكثر من االستراتيجيات األخرى .ـ أنه ال توجد عالقة بين االستراتيجيات المستعملة وأداء المعلمين باللغة المدرسية شفويا وكتابيا ـ وأنها ال توجد فروق ذات داللة إحصائية بين الناطقين بالعامية العربية و الناطقين بالقبائلية في البنية الصوتية لكن هناك فروقا دالة إحصائيا بينهما في البنيتين النحوية والصرفية لكنها تعود إلى عوامل اخرى ذاتية وبيداغوجية .وأسرية .واستنتجنا ان مستوى المتعلمين من العينتين بلغة التعليم لم يرتق إلى الكفاءات المنشودة في المنهاج المدرسي.  The Role of the Mother Tongue in Learning Standard Arabic at the Primary Stage in the Algerian School 出版年份: 2012 作者: Khaled Abdel Salam 机构作者: Farhat Abbas Setif University Our study has two mean objectives: To determine the first language consequences, whatever they are general, Arabic, or Kabyle, in the learning of school language at different vocabulary, singular, grammar, and, conjugation structures, therefore, exploring if they are helping factors in the learning process or hampering it. To identify the cognitive strategies used by the novices in their learning process in relation to their language performance and errors made in the oral and written expression. In order to deal with this situation, we utilized the descriptive analytical method, in which we had chosen randomly two samples composed of 90 scholars (45 scholars speaking general Arabic language, and 45 scholars speaking Kabyle language), on which we administered two tests, one in the form of an interview about personal and health informations, and the other one about the environment conservation. After, we had analysed the content of the responses, via the extraction of the language errors expanded, and categorising them to different styles or patterns, and computing their frequencies, and explaining them, we founded the following results: Whatever, the first language is general, Arabic or Kabyle, it has a big consequence over all the language structures, therefore, making the scholars language not different from them. According to these results, we can conclude that these factors are not considered as helping factors in the learning process. There is a tendency for the novices to utilize more, both of the revising strategies of courses and the deduction strategy compared to the others. there are no significant differences between scholars speaking general Arabic language and scholars speaking kabyle language in the vocabulary structure, but, there are significant differences between these two samples on the grammatical and conjugational structures, related to personal, pedagogical and familiar factors. According to these results, we can conclude that the language level of the novices on both samples is not related to the abilities required by the school system.
The Role of the Mother Tongue in Learning Standard Arabic at the Primary Stage in the Algerian School 出版年份: 2012 作者: Khaled Abdel Salam 机构作者: Farhat Abbas Setif University Our study has two mean objectives: To determine the first language consequences, whatever they are general, Arabic, or Kabyle, in the learning of school language at different vocabulary, singular, grammar, and, conjugation structures, therefore, exploring if they are helping factors in the learning process or hampering it. To identify the cognitive strategies used by the novices in their learning process in relation to their language performance and errors made in the oral and written expression. In order to deal with this situation, we utilized the descriptive analytical method, in which we had chosen randomly two samples composed of 90 scholars (45 scholars speaking general Arabic language, and 45 scholars speaking Kabyle language), on which we administered two tests, one in the form of an interview about personal and health informations, and the other one about the environment conservation. After, we had analysed the content of the responses, via the extraction of the language errors expanded, and categorising them to different styles or patterns, and computing their frequencies, and explaining them, we founded the following results: Whatever, the first language is general, Arabic or Kabyle, it has a big consequence over all the language structures, therefore, making the scholars language not different from them. According to these results, we can conclude that these factors are not considered as helping factors in the learning process. There is a tendency for the novices to utilize more, both of the revising strategies of courses and the deduction strategy compared to the others. there are no significant differences between scholars speaking general Arabic language and scholars speaking kabyle language in the vocabulary structure, but, there are significant differences between these two samples on the grammatical and conjugational structures, related to personal, pedagogical and familiar factors. According to these results, we can conclude that the language level of the novices on both samples is not related to the abilities required by the school system.  Spotlight on Basic Education Completion and Foundational Learning in Africa, 2022: Born to Learn 出版年份: 2022 机构作者: UNESCO | Association for the Development of Education in Africa (ADEA) | African Union This publication is the first in a three-part Spotlight series. It is produced by a partnership between the Global Education Monitoring Report, the Association for the Development of Education in Africa and the African Union.The report focuses on why learning levels in the region are low. All children are born to learn yet only one in five children in Africa who reach the end of primary school achieve the minimum proficiency level required to continue their education and fulfil their potential. Combining completion and learning statistics, the report shows that children in Africa are at least five times less likely than children in the rest of the world to be prepared for the future.Given the historically low levels of learning on the continent, fresh thinking is needed to translate the CESA and SDG 4 commitments into focused, coordinated, well-informed and appropriately funded actions. The report contains eight policy-oriented recommendations for driving change.
Spotlight on Basic Education Completion and Foundational Learning in Africa, 2022: Born to Learn 出版年份: 2022 机构作者: UNESCO | Association for the Development of Education in Africa (ADEA) | African Union This publication is the first in a three-part Spotlight series. It is produced by a partnership between the Global Education Monitoring Report, the Association for the Development of Education in Africa and the African Union.The report focuses on why learning levels in the region are low. All children are born to learn yet only one in five children in Africa who reach the end of primary school achieve the minimum proficiency level required to continue their education and fulfil their potential. Combining completion and learning statistics, the report shows that children in Africa are at least five times less likely than children in the rest of the world to be prepared for the future.Given the historically low levels of learning on the continent, fresh thinking is needed to translate the CESA and SDG 4 commitments into focused, coordinated, well-informed and appropriately funded actions. The report contains eight policy-oriented recommendations for driving change.  Inequidad de género en los logros de aprendizaje en educación primaria ¿Qué nos puede decir TERCE?; resumen ejecutivo 出版年份: 2016 作者: Denisse Gelber, Ernesto Treviño, Pamela Inostroza 机构作者: UNESCO Santiago This premise of work clearly establishes that promoting learning opportunities for all will be one of the priorities in the Education 2030. Within this framework, UNESCO Santiago has its own instrument that allows delivering diagnosis and analysis in depth about the learning inequality within the region; the Thrid Regional Comparative and Explanatory Study, TERCE - carried out by the Latin American Laboratory for Assessment of the Quality of Education, LLECE, body bringing together 15 countries and coordinated by our Office.
Inequidad de género en los logros de aprendizaje en educación primaria ¿Qué nos puede decir TERCE?; resumen ejecutivo 出版年份: 2016 作者: Denisse Gelber, Ernesto Treviño, Pamela Inostroza 机构作者: UNESCO Santiago This premise of work clearly establishes that promoting learning opportunities for all will be one of the priorities in the Education 2030. Within this framework, UNESCO Santiago has its own instrument that allows delivering diagnosis and analysis in depth about the learning inequality within the region; the Thrid Regional Comparative and Explanatory Study, TERCE - carried out by the Latin American Laboratory for Assessment of the Quality of Education, LLECE, body bringing together 15 countries and coordinated by our Office.  Региональный обзор: Центральная и Восточная Европа и Центральная Азия 出版年份: 2015 机构作者: UNESCO В настоящем региональном обзоре, где рассматривается прогресс, достигнутый с 2000 г., кратко излагаются ответы на важнейшие вопросы, которым посвящен Всемирный доклад по мониторингу (ВДМ) ОДВ за 2015 г. В ВДМ за 2015 г. показано, что, несмотря на прогресс, цели образования для всех еще не до конца достигнуты, в том числе в Центральной и Восточной Европе и Центральной Азии.
Региональный обзор: Центральная и Восточная Европа и Центральная Азия 出版年份: 2015 机构作者: UNESCO В настоящем региональном обзоре, где рассматривается прогресс, достигнутый с 2000 г., кратко излагаются ответы на важнейшие вопросы, которым посвящен Всемирный доклад по мониторингу (ВДМ) ОДВ за 2015 г. В ВДМ за 2015 г. показано, что, несмотря на прогресс, цели образования для всех еще не до конца достигнуты, в том числе в Центральной и Восточной Европе и Центральной Азии.  План действий Всемирная программа образования в области прав человека : Первый этап 出版年份: 2006 机构作者: UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights The Plan of Action for the first phase (2005-2007) of the World Programme was adopted by all United Nations Member States in July 2005. It proposes a concrete strategy and practical guidance for implementing human rights education in primary and secondary schools. On 10 December 2004, the General Assembly of the United Nations proclaimed the World Programme for Human Rights Education (2005-ongoing) to advance the implementation of human rights education programmes in all sectors. Building on the foundations laid during the United Nations Decade for Human Rights Education (1995-2004), this new initiative reflects the international community’s increasing recognition that human rights education produces far-reaching results. By promoting respect for human dignity and equality and participation in democratic decision-making, human rights education contributes to the long-term prevention of abuses and violent conflicts. To help make human rights a reality in every community, the World Programme seeks to promote a common understanding of the basic principles and methodologies of human rights education, to provide a concrete framework for action and to strengthen partnerships and cooperation from the international level down to the grass roots.
План действий Всемирная программа образования в области прав человека : Первый этап 出版年份: 2006 机构作者: UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights The Plan of Action for the first phase (2005-2007) of the World Programme was adopted by all United Nations Member States in July 2005. It proposes a concrete strategy and practical guidance for implementing human rights education in primary and secondary schools. On 10 December 2004, the General Assembly of the United Nations proclaimed the World Programme for Human Rights Education (2005-ongoing) to advance the implementation of human rights education programmes in all sectors. Building on the foundations laid during the United Nations Decade for Human Rights Education (1995-2004), this new initiative reflects the international community’s increasing recognition that human rights education produces far-reaching results. By promoting respect for human dignity and equality and participation in democratic decision-making, human rights education contributes to the long-term prevention of abuses and violent conflicts. To help make human rights a reality in every community, the World Programme seeks to promote a common understanding of the basic principles and methodologies of human rights education, to provide a concrete framework for action and to strengthen partnerships and cooperation from the international level down to the grass roots.  Feature or footnote ? Teacher's attitudes toward the teaching of the Holocaust in primary schools in Scotland The question of teaching controversial and difficult issues in primary schools remains itself controversial. This article discusses the area of teaching the Holocaust in primary schools in Scotland by examining its relevance to the primary curriculum and reporting on survey and interview research amongst a sample of primary teachers in Scotland. Based on limited research, this paper suggests that the Holocaust is appropriate for primary pupils, provides insight into the reactions of parents and colleagues and shows that Holocaust history in Scottish primary schools is set firmly within the contexts of Anne Frank and World War Two. We find that there are significant barriers to its teaching, yet most of these can be successfully overcome. (By the author)
Feature or footnote ? Teacher's attitudes toward the teaching of the Holocaust in primary schools in Scotland The question of teaching controversial and difficult issues in primary schools remains itself controversial. This article discusses the area of teaching the Holocaust in primary schools in Scotland by examining its relevance to the primary curriculum and reporting on survey and interview research amongst a sample of primary teachers in Scotland. Based on limited research, this paper suggests that the Holocaust is appropriate for primary pupils, provides insight into the reactions of parents and colleagues and shows that Holocaust history in Scottish primary schools is set firmly within the contexts of Anne Frank and World War Two. We find that there are significant barriers to its teaching, yet most of these can be successfully overcome. (By the author) 